Translate this page into:
A case of pycnodysostosis presented with pathological femoral shaft fracture
*For correspondence: shailendra81mamc@gmail.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Pycnodysostosis is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder of bone in which the enzyme cathepsin K is mutated which maps on chromosome 1q21 causing osteoclast dysfunction. A 15-year old male patient of 140 cm height presented to the Department of Orthopaedics, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India, in November 2012 with pathological fracture in shaft of femur (Fig. 1). On the basis of clinical and radiological findings, he was diagnosed as a case of pycnodysostosis. The patient had history of recurrent fractures with normal bone healing, open fontanelles, short stature, short finger tips, flat and grooved nails (Fig. 2), micrognathia, and irregular teeth with hypodontia. The patient had normal intramedullary haematopoesis and no hepatospleenomegaly. Radiological evaluation of patient revealed generalized osteopetrosis, short distal phalanges (Fig. 3), obtuse angle of mandible and open fontanelles (Fig. 4). He was managed conservatively by upper tibial skeletal traction and Thomas knee splint and showed normal bone healing pattern.
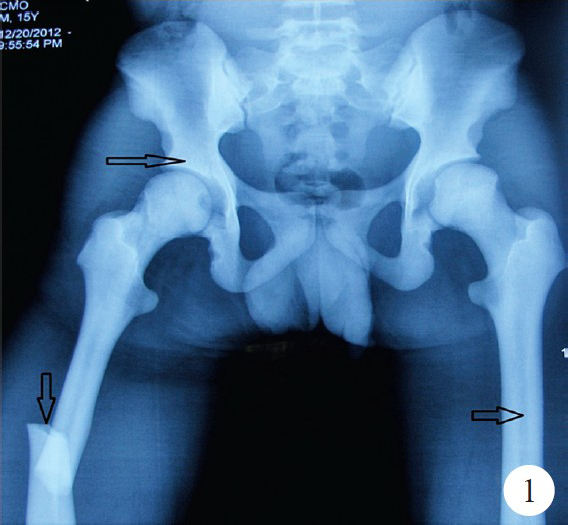
- X-ray both hips with thigh showing sclerotic bones, pathological fracture in shaft femur and narrow medullary canal (arrows).
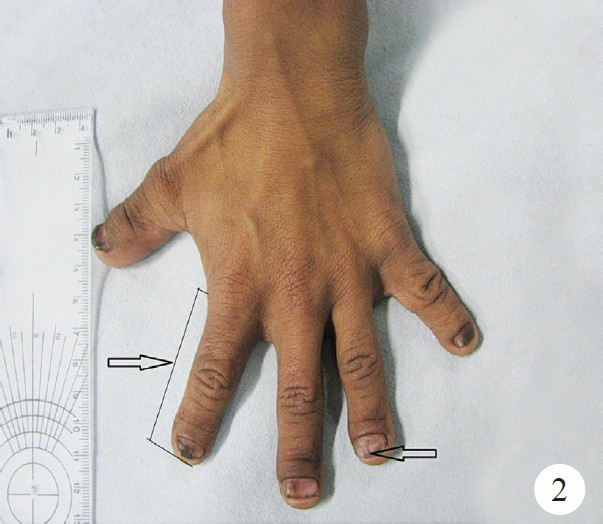
- Small fingers and grooved nails (arrow).
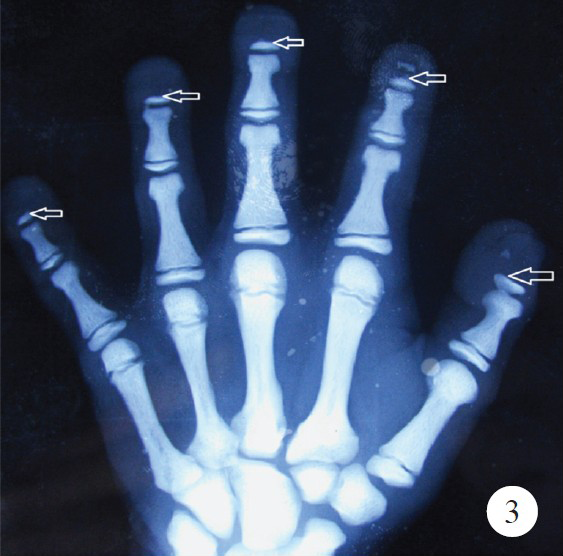
- X-ray of hand showing hypoplastic distal phalynx (arrows).
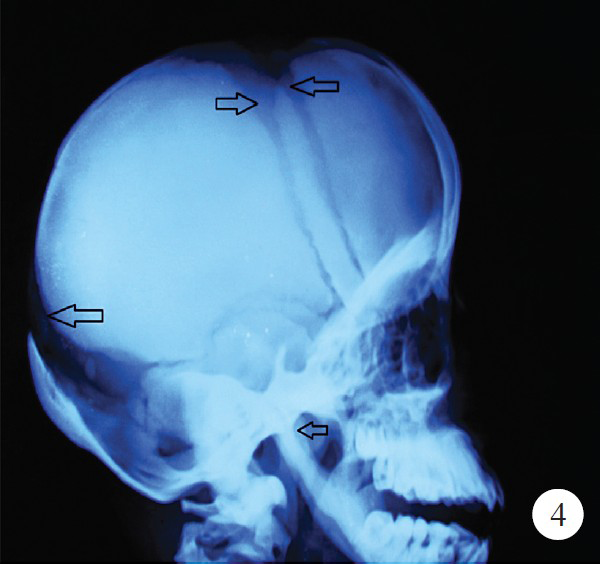
- X-ray of skull showing open anterior and posterior fontanelle and obtuse angle of mandible (arrows).





