Translate this page into:
Unusual cause of hypersensitivity pneumonitis with characteristic head-cheese sign
*For correspondence: diptigothi@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A 53 yr old non-smoker female† presented to ESIC Hospital & PGIMSR, Basaidarapur, New Delhi, India, with complaints of dyspnoea grade 3 and cough with minimal expectoration. The patient was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and hypertension three months ago and was on oral drugs for the same. On examination, the respiratory rate was 18 and the saturation was 95 per cent on room air. Six minute walk distance was 130 m and saturation was 82 per cent after exercise. Baseline investigations were within normal limits. High-resolution computed tomography chest (Fig. 1) was done which showed 'head-cheese' sign, cysts and nodules with feeding vessel sign. The patient had no exposure to birds but her house was next to an open sewer and there was no ventilation. Spirometry showed obstructive lung disease with air trapping. Transbronchial lung biopsy was done which showed ill-defined granulomas (Fig. 2). A diagnosis of acute on chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to sewage exposure was made. The patient improved with steroid and change of residence. The follow up spirometry after three months showed improvement.
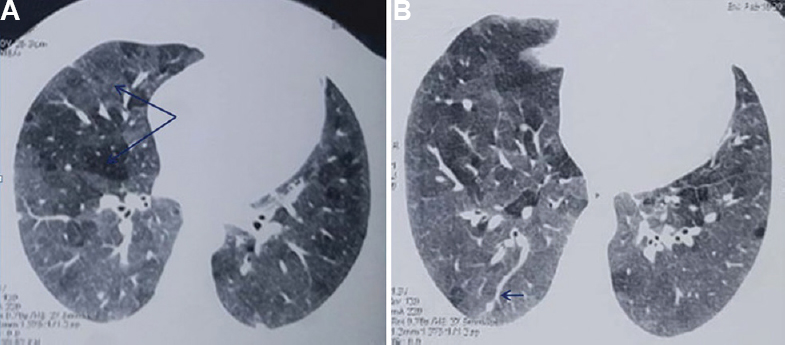
- High-resolution computed tomography of chest axial section at the level of lower lobe bronchus. (A) Shows head-cheese sign (arrows) and (B) showing feeding vessel sign (arrow).
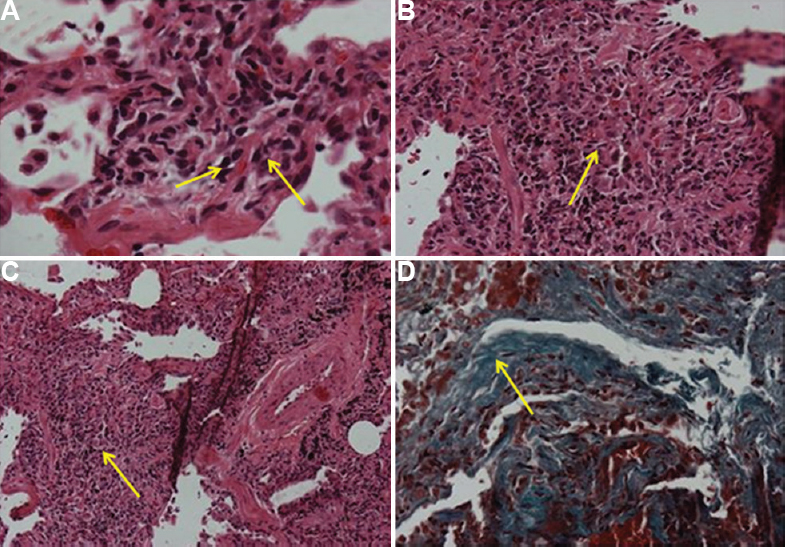
- Histopathology images of transbronchial lung biopsy under low and high power field. (A) Multifocal ill-defined granulomas (arrows). (B) Acute on chronic inflammation (arrow). (C) Perivascular granuloma (arrow) and (D) Interstitial fibrosis (arrow).
Conflicts of Interest: None.





