Translate this page into:
Unmet need for contraception among married women in an urban area of Puducherry, India
Reprint requests: Dr Hemant Deepak Shewade, The International Union Against Tuberculosis & Lung Disease South East Asia Office, New Delhi 110 016, India e-mail: hemantjipmer@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
Unmet need for contraception remains a national problem. The study was conducted in an urban area of Puducherry, India, among the eligible couples to assess the unmet need for contraception and to determine the awareness and pattern of use of contraceptives along with the socio-demographic factors associated with the unmet needs for contraception.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included eligible couples with married women in age group of 15-45 yr as the study population (n=267). Probability proportional to size sampling followed by systematic random sampling was used. A pre-tested questionnaire was administered to collect data from the respondents. Double data entry and validation of data was done.
Results:
Unmet need for contraception was 27.3 per cent (95% CI: 22.3-33); unmet need for spacing and limiting was 4.9 and 22.5 per cent, respectively. Among those with unmet need (n=73), 50 per cent reported client related factors (lack of knowledge, shyness, etc.); and 37 per cent reported contraception related factors (availability, accessibility, affordability, side effects) as a cause for unmet need.
Interpretation & conclusions:
Our study showed a high unmet need for contraception in the study area indicating towards a necessity to address user perspective to meet the contraception needs.
Keywords
awareness
contraception
cross-sectional study
prevalence
questionnaire
women
Globally, the prevalence of contraceptive use has been increasing, but the unmet need for contraception still remains a problem1. The contraceptive and non-contraceptive benefits of mordern contraceptives outweigh the risks2. According to the National Family Health Survey-3 (NFHS-3)3, the national figure for unmet need is 13 per cent. According to the District Level Household and Facility Survey-3 (DLHS-3)4, unmet need of contraception in India is 21.3 per cent, with 7.9 per cent for spacing and 13.4 per cent for limiting. Unmet need for contraception in Puducherry is about 19.8 per cent, of which 6.5 per cent is for spacing and 13.3 per cent for limiting4. Local health planners are in a prime position to revise feasible context-specific activities to decrease the constraint and meet the needs5.
This study was carried out among the eligible couples of Muthialpet, Puducherry, India in 2013 with the objectives to assess the unmet need for contraception and determine the awareness and pattern of use of contraceptives, as also to identify socio-demographic factors associated with unmet needs for contraception.
Material & Methods
The study setting for this cross-sectional study was a service area falling under Primary Health Centre (PHC) Muthialpet, Puducherry, India. Muthialpet is an urban area in Puducherry having a population of 45000. About half of the population lives in slums areas which are as good as the other non-slum areas of Muthialpet in aspects of hygiene, housing, sanitation, water supply, etc. Eligible couples with married women in the age group of 15-45 yr, residing in Muthialpet, were the study population. Study period was from January to September 2013.
Operational definitions for unmet need for spacing, limiting and unfelt need used in the study were as per DLHS-34. The study protocol was approved by the institutional ethics committee and written informed consent was obtained from the participants.
Study tool: The interviewer administered questionnaire used in the study was pretested on 10-20 married women of reproductive age belonging to the study population (but not in the final sample) and with an expert. The questionnaire had two parts: Part I included respondent/ husband/ family particulars, marital history and contraceptives/ fertility status. Modified Kuppuswamy scale, 20126 was used to assess socio-economic class. Part II included questions on reasons for not using contraception among those with unmet need.
Sample size was calculated for confidence interval estimation of single proportion using n master sample size calculator v.2.0 developed by the Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore. Assuming the unmet need for Muthialpet to be 19.8 per cent (DLHS-3-Puducherry), absolute precision of 5 per cent and a 95% confidence interval, the sample size to be surveyed was 244. Sample size planned was approximately 4 per cent of the study population in Muthialpet (7200 eligible couples). The PHC area was divided into 48 anganwadi areas. Using probability proportional to size (PPS) method, 15 anganwadis were selected. From each selected anganwadi area, 20 households were selected using systematic random sampling. If there were more than one eligible in a household, Kish Grid was used to select one respondent.
Statistical analysis: Data collected were entered inEpiData v.3.1 software (EpiData Association, Odense, Denmark). Double data entry and validation of the data was done to correct data entry errors. EpiData Analysis v2.2.2.182 (EpiData Association, Odense, Denmark) was used for descriptive statistics. SPSS v17 (Chicago, USA) was used for analytical statistics. Binomial logistic regression was used to analyse factors associated with unmet need.
Results
Two hundred and sixty seven married women in reproductive age group were interviewed. Their mean age, age at marriage and marriage duration were 33.5 ± 6.9, 21.7 ± 3.6, 11.8 ± 7.9 yr, respectively. Around 89 per cent were educated up to high school or above; 3 per cent were illiterate or did not complete primary education. Median family income per month was 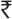 10000; none was from lower socio-economic class. Around 69 per cent were from nuclear families and 85 per cent were Hindu. Around 17 per cent of women gave history of medical termination of pregnancy (MTP).
10000; none was from lower socio-economic class. Around 69 per cent were from nuclear families and 85 per cent were Hindu. Around 17 per cent of women gave history of medical termination of pregnancy (MTP).
Of the 267 women of reproductive age group, 157 (58.8%, 95% CI: 52.8-64.5) eligible couples were using contraceptives. Unmet need for contraception was 27.3 per cent (95% CI: 22.3-33); unmet needs for spacing and limiting were 4.9 per cent (95% CI: 2.9-8.2) and 22.5 per cent (95% CI: 17.5-27.5), respectively. Among those who had ever used contraception, unmet need for contraception was 12 per cent, which contributed to 50.6 per cent of all the unmet need.
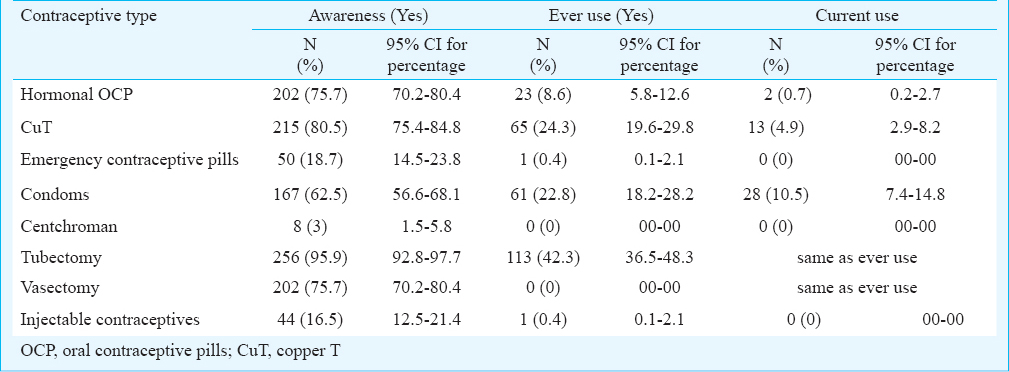
Awareness levels were >60 per cent for all temporary contraceptives except emergency contraceptive pills (18.7%), injectable contraceptives (16.5%) and centchroman (3%); it was >75 per cent for tubectomy and vasectomy (Table I).
Regression analysis (binomial logistic regression: forward LR method) did not reveal any significant difference in distribution of socio-demographic factors among users of contraception and those with unmet need for contraception.
Among those with unmet need (n=73), approximately 50 per cent reported client related factors (lack of knowledge, shyness, etc.) as a cause for unmet need; and 37 per cent reported contraception related factors: availability, accessibility, affordability, side effects (Table II).

Discussion
There was a high unmet need for contraception in Muthialpet region of Puducherry which was higher compared to the figures given by DLHS-34 for Puducherry, i.e. 19.8 per cent; and figures for India given by NFHS-33, i.e. 13 per cent. Similar studies conducted elsewhere have given the following figures for unmet need: 44 per cent in a tribal area of Maharashtra7, 41.6 per cent in Haryana8, 25.4 per cent in a resettlement colony of New Delhi9, 21.7 per cent in Gwalior10, 22.4 per cent in Bangladesh11, 16.3 per cent in Jordan12, 17.4 per cent in Iran13, and 20 per cent in Ethiopia14.
Awareness level and use pattern were similar to the national figures: tubectomy and condoms were the most common contraceptives currently used4. Sample size calculation was not carried out for the association of socio-demographic factors with contraceptive use. Inadequate sample size for carrying out this analysis could be the reason for insignificant results. Other studies have identified that gender preference1516, lower level of education78912171819, women's occupation as homemaker17, number of children ever born79121518 and age71012 were the factors associated with unmet need.
High awareness levels and high unmet need indicate that there are certain user perspectives among non-users which have not been addressed. Previous studies have identified certain factors as a reason for not using contraceptive such as irregular menstruation with oral pills and weakness15, family and husband opposition812, and lack of information8.
The questionnaire used in this study to collect data was tested for reliability and validity. Double data entry and validation of data was done to remove any data entry errors. The limitation of this study was that the sample size was not calculated for the regression analysis. Also information from the male partners was not collected.
In conclusion, our study indicated a high unmet need for contraception in the area with a scope to decrease constraints and address user perspective to meet the contraception needs.
Acknowledgment
Author acknowledge Dr Jeyashree K., Department of Community Medicine, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh for technical inputs on improving the content validity of the questionnaire, Dr K.C. Panigrahi, Head, Department of Community Medicine, Indira Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute (IGMCRI), Puducherry for his guidance throughout the study period and the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Puducherry for giving permission to carry out the study. Authors thank the Anganwadi workers, supervisors and Child Development Project Officer (CDPO) under Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS) for their support in implementing the study. This research project was selected under ICMR Short Term Studentship (STS) programme 2013.
References
- National, regional, and global rates and trends in contraceptive prevalence and unmet need for family planning between 1990 and 2015: a systematic and comprehensive analysis. Lancet. 2013;381:1642-52.
- [Google Scholar]
- IIPS. National family health survey (NFHS-3), 2005-06. 2007. Mumbai: International Institute for Population Studies; Available from: http://www.mohfw.nic.in/nfhs3/index.htm
- [Google Scholar]
- District level household and facility survey III 2007- 08 (DLHS III). Ministry of health and family welfare, Government of India. Available from: http://www.rchiips.org/pdf/INDIA_REPORT_DLHS-3.pdf
- [Google Scholar]
- Context-specific, evidence-based planning for scale-up of family planning services to increase progress to MDG 5: health systems research. Reprod Health. 2012;9:27.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy's socio economic scale updating income ranges for the year. Indian J Public Health. 2012;56:103-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Unmet needs for contraception in married women in a tribal area of India. Malaysian J public Health Med. 2010;10:44-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- A study on the extent and reasons of unmet need for family planning among women of reproductive age group in rural area of Haryana. Internet J Health. 2009;12(1)
- [Google Scholar]
- Study of unmet need for family planning in a resettlement colony of east Delhi. Health Popul: Perspect Issues. 2007;30:124-33.
- [Google Scholar]
- A study to assess the unmet needs of family planning in Gwalior district and to study the factors that helps in determining it. Natl J Community Med. 2011;2:29-31.
- [Google Scholar]
- Unmet need for family planning among rural women in Bangladesh. J Dhaka Med Coll. 2010;19:11-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Demographic profile and predictors of unmet need for family planning among Jordanian women. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2007;33:53-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Contraceptive use and unmet need for family planning in Iran. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2013;121:157-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- Family planning knowledge, attitude and practice among married couples in Jimma Zone, Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2013;8:e61335.
- [Google Scholar]
- Attitude of women towards family planning methods and its use - study from a slum of Delhi. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2005;3:259-62.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevalence and determinants of unmet need for family planning in a district of eastern region of Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2006;4:203-10.
- [Google Scholar]
- Factors affecting unmet need for family planning in Eastern Sudan. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:102.
- [Google Scholar]
- Variations in unmet need for contraception in zambia: does ethnicity play a role? J Biosoc Sci. 2014;46:294-315.
- [Google Scholar]
- Family planning use among urban poor women from six cities of Uttar Pradesh, India. J Urban Health. 2012;89:639-58.
- [Google Scholar]






