Translate this page into:
Subcutaneous cysticercosis
*For correspondence: alladimohan@svims.gov.in alladimohan@gmail.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
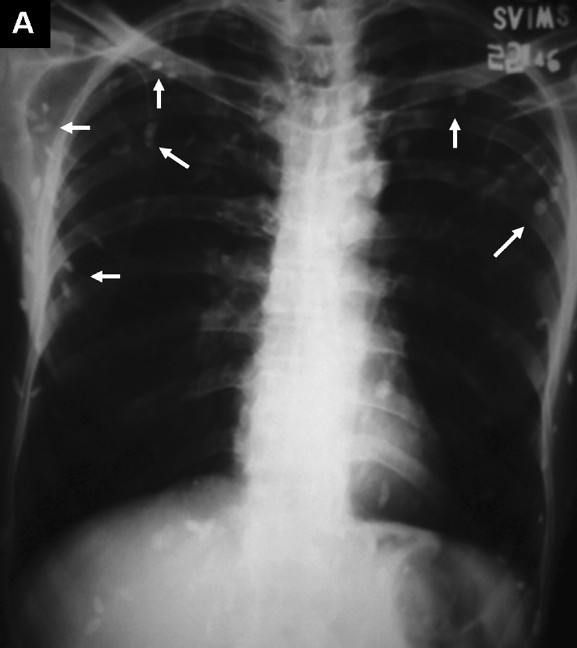
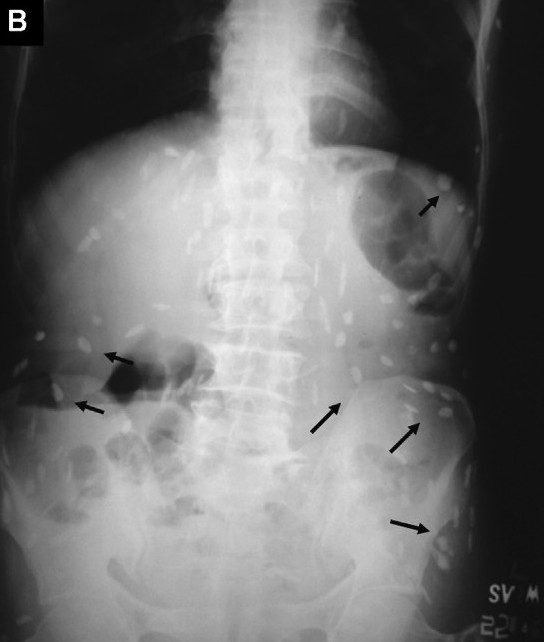
A 50-year-old male presented to the emergency service for evaluation of acute onset abdominal pain. The chest radiograph (Fig. A, white arrows) and plain radiograph of the abdomen (erect posture) (Fig. B, black arrows) revealed classical multiple cigar-shaped calcified densities suggestive of subcutaneous cysticercosis. Human cysticercosis develops due to the ingestion of the eggs of Taenia solium; sometimes autoinfection may occur if individuals harbouring egg-producing tapeworms ingest eggs derived from their own faeces. Surgical excision is generally limited for histopathological confirmation of the diagnosis. Asymptomatic calcified cysticerci are better left alone.