Translate this page into:
Profile of inhalant users seeking treatment at a de-addiction centre in north India
Present addresses: *Department of Psychiatry, NIMS Medical Collge & Hospital, Jaipur, India **All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, India
Reprint requests: Dr S.K. Mattoo, Professor, Department of Psychiatry Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research, Chandigarh 160 012, India e-mail: skmattoo@ymail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
Inhalants are substances whose chemical vapors are inhaled to produce euphoric, disinhibiting, and exciting effects. Data on inhalant abuse in India are relatively scarce. We report the demographic and clinical profile of inhalant users among the treatment seekers at a Drug De-addiction and Treatment Centre in north India.
Methods:
The records of treatment seekers at the Drug De-addiction and Treatment Centre, over 10 years (2002-2011) were scanned to identify 92 cases reporting inhalant use. Of these 92 cases, the complete record files were available for 87 (94.6%) cases. These case files were reviewed and the relevant data were collected and analyzed.
Results:
Over the study period of 10 years, the number of cases with inhalant abuse per year rose steadily to peak at 20 cases (4.08% of new cases) in 2006 and then stabilized at 1-3 per cent of new cases annually. Of the 87 cases studied, all were males with a mean age of 18.9±4.12 yr, mean education of 9.8±3.42 yr and mean family income of 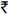 7676±7343.15 (median:
7676±7343.15 (median: 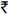 5000). Majority of subjects were unmarried (89.7%), urban resident (79.3%), and from a nuclear family (78.2%). About half of the subjects were students (50.6%). The most common inhalant used was typewriter correction fluid (73.6%) followed by typewriter diluent fluid (19.5%) and glue (6.9%). The most common reason for initiation was curiosity. The mean age of onset of inhalant use was 16.3±4.22 yr. Most subjects fulfilled the criteria for inhalant dependence (85.1%). Psychiatric co-morbidity and the family history of substance dependence were present in 26.4 and 32.9 per cent subjects, respectively. Majority of the subjects reported drug related problems, occupation and finance being the worst affected.
5000). Majority of subjects were unmarried (89.7%), urban resident (79.3%), and from a nuclear family (78.2%). About half of the subjects were students (50.6%). The most common inhalant used was typewriter correction fluid (73.6%) followed by typewriter diluent fluid (19.5%) and glue (6.9%). The most common reason for initiation was curiosity. The mean age of onset of inhalant use was 16.3±4.22 yr. Most subjects fulfilled the criteria for inhalant dependence (85.1%). Psychiatric co-morbidity and the family history of substance dependence were present in 26.4 and 32.9 per cent subjects, respectively. Majority of the subjects reported drug related problems, occupation and finance being the worst affected.
Interpretations & conclusions:
Our results showed that the inhalant users were mostly urban youth belonging to middle socio-economic class families. The principal sources of inhalant abuse were the commonly available substances like typewriter correction fluids and majority of the subjects initiated it out of curiosity. Nearly three-fourth of the subjects used some other substance of abuse in addition, tobacco being the most common. In view of associated drug related problems, there is a need for strategies to prevent this emerging health care problem.
Keywords
Abuse
dependence
inhalant
inhalant use disorders
volatile solvents
As substances of abuse, inhalants are chemicals whose vapors can be intentionally inhaled to produce psychoactive effect. These are classified into four broad groups: volatile solvents (e.g., typewriter correction fluid, typewriter diluent fluid, glue, paint thinner and gasoline), aerosols (e.g., hair spray and spray paint), gases (nitrous oxide and ether), and nitrites (like amyl-, butyl-, and isobutylnitrites)1. The inhalants produce an instant and short-lived high with euphoria and disinhibition. A retrospective review of symptomatic inhalant exposure in a spanish population showed involvement of the central nervous system (CNS) (62.8%), gastrointestinal (8.1%), cardiovascular (8.1%), respiratory (2.9%), peripheral nervous system (1.1%), renal (1.1%), haematological (1.1%), hepatic (1.7%), and other systems/organs (13.1%)2. Easy availability of these substances to children and adolescents has become an issue of great concern. A study from Egypt done in a random sample of 120 street children aged 10 to 18 yr found that 91 per cent of the subjects reported abuse of volatile solvents for the reasons that they were inexpensive, legal, and easy to procure3.
The prevalence of inhalant use has been reported approximately at 1 per cent in the general population, 7 per cent among high school students and still higher for street children in Mexico4. One study from the USA reported 10-20 per cent of adolescents surveyed annually over the 30 years with a history of inhalants abuse5. A cross-sectional survey found that inhalants were the first or second most commonly reported substances used after alcohol and cigarettes among school attending youth in all nine participating countries (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, and Uruguay), with lifetime prevalence ranging from 2.67 per cent in Paraguay to 16.55 per cent in Brazil6.
Serious mental health and substance use problems commonly co-occur with inhalant use disorders (IUD)578. Early-onset inhalant abuse is associated with various deleterious outcomes: increased risk for inhalant dependence, subsequent heroin and injection drug use, other psychoactive drug use, and mental health problems including mood disorders and anti-social behaviour, especially interpersonal violence and early-onset conduct problems5910. Astrong relationship has been suggested between inhalant use and sensation seeking811. Other reported risk factors include domestic violence, a dictatorial father, presence of step-parents, migrant status, low levels of parental education, parental drug use, familial neglect, parental discord and lack of supervision35811.
Most of the available research on the socio-demographic and clinical profile of subjects with IUDs and their association with other substances is from the western countries. The relatively meager published research from India shows the following limitations: small sample size, mostly based on children, especially the street children, and a few case reports or case series7121314151617181920212223242526. There are no national statistics on inhalant use disorders in India. The Indian National Household Survey on Drug Use, which surveyed 8,587 children aged 12-18 yr, did not seek information on inhalants27. A few studies on inhalant users in de-addictions settings have reported that most subjects were adolescents with mean age of initiation of inhalant use 11-18 yr. The commonest cause of first use reported by the subjects was experimentation/curiosity. Tobacco has been found to be the most commonly associated substance of use71213. Majority of the subjects had poor social support16171819.
Considering the slow but definitive emergence of this new health care problem, the present study was aimed to report the demographic and clinical profile of inhalant users among those seeking treatment at a de-addiction center in north India.
Material & Methods
The study was conducted at the Drug De-addiction and Treatment Centre (DDTC), Department of Psychiatry, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India. The study had the approval of the institutional research ethics committee. This was a retrospective chart review study. To meet the study objectives, the case files of all subjects with inhalant use reporting to the DDTC of our Institute were studied for the required data. Over 10 years (2002- 2011), 92 of the 5393 (1.71%) new registrants had undergone a detailed diagnostic assessment for reported inhalant use. Of these 92, complete case records were available for 87 (94.6%) cases. The study relevant data were collected from the case files, tabulated on a pre-formed semi-structured proforma and analyzed. An earlier study from our centre has reported on 21 of these 92 cases7.
Measures: The study relevant data included socio-demographic and clinical details as recorded in the semi-structured proforma, developed and routinely used at the DDTC. All the measures used were clinician rated.
Socio-demographic details covered age, sex, marital status (single, married, divorced, widowed), educational status (years of formal education), family income, occupational status (student, working or unemployed), religion (Hinduism, Sikhism, Christianity or Islam), family type (nuclear, extended or joint), locality, distance from the DDTC and the source of referral.
Clinical details covered the types of substance use, age of onset, durations of use and dependence, and primary reason for initiation of inhalants measured in terms of curiosity, peer pressure and source of alleviating frustration. Data regarding other substance use, psychiatric and physical co-morbidities as diagnosed in the case files and relevant data on treatment given, follow ups and status at the last follow up were also collected.
Additional recorded details included the following:
Social support - measured on a 4-point scale from poor (no support system), minimal (support from only one source; family, network or society), fair (support from two sources) to good social support (support from three or more sources).
High risk behaviours - Data regarding sexual practices (like unprotected sex with multiple partners, sex with commercial sex workers) and intra-venous drug use were also recorded.
Drug related harm - measured on a 4-point scale from 0 (none) to 3 (severe) for seven domains: health (physical or psychiatric), occupation (absenteeism, suspension, unemployment, etc.), finance (debts, etc.), legal (arrests), family (impaired inter-personal relationships), marital (separation, divorce) and social (restriction of social circle, ostracism).
Motivation to quit inhalants was measured on a 5-point grading: ‘0’ for poor motivation, ‘1’ for motivation between poor and superficial, ‘2’ for superficial, ‘3’ for motivation between superficial and fair, and ‘4’ for fair/good motivation.
Evaluation of social support, high risk behaviours, drug related harm, and motivation to quit inhalants was clinician rated, based on global clinical impression, and part of the routine detailed evaluation done for all subjects in DDTC.
Abstinence, lapse, relapse, or continued use without abstinence as recorded at the last follow up, was considered as the primary outcome measures. The definitions used were: Abstinence: no substance intake; Lapse: use of the substance less than that for relapse; Relapse: re-emergence of substance dependence as per the ICD-1028.
Statistical analysis: Descriptive statistics were used for the demographic and clinical variables. Non-parametric test (chi-square test) was applied to see relationship between nominal and ordinal data. Parametric test (student t-test) was applied for the continuous variables. Simple binary logistic regression analysis with enter method was used to study the relationship among independent variables which were more frequently present in subjects who were followed up and who remained abstinent (improved) at follow up. Analysis was done by SPSS version 14 for Windows (Chicago, Illinois, USA).
Results
The first case with inhalant use was registered in 2002. By 2011, a total of 92 cases were registered, with registrations ranging 1-20 (median of 6.5 cases) and accounting for 0.24-4.08 per cent (median of 1.16%) of the annual new case registrations. After the peak of 20 cases (4.08%) in 2006, there were 1-3 per cent of the new cases reporting inhalant use annually.
The study group (N=87) had a mean age of 18.89 ± 4.12 yr (range: 12-31 yr), education for 9.84 ± 3.42 yr (range: 0-16 yr), and monthly family income of 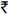 7675.86 ± 7343.15 (range:
7675.86 ± 7343.15 (range: 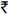 800-40000; median:
800-40000; median: 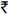 5000). All were males, with 78 (89.7%) of them being unmarried. While 44 (50.6%) were students, and 11 (12.6%) were working, the remaining 32 (36.8%) were unemployed. The religious affiliations were: Hindu 65 (74.7%), Sikh 17 (19.5%), and others 5 (5.7%). The family types were: nuclear 68 (78.2%), extended 11 (12.6%) and joint 8 (9.2%). Social support was assessed as fair to good in 51 (58.6%) (fair in 46, 52.9%) and minimal to poor in 36 (41.3%) (minimal in 35, 40.2%) subjects. Urban subjects were in majority 69 (79.3%), with 56 (64.4%) of them residing within 40 km of the DDTC. Most of the subjects were brought by their family members 70 (80.5%); only a few had come on their own 5 (5.7%). Demographic data of missing records (N=5) and available case records (N=87) were comparable in gross terms; small number of missing records precluded the application of inferential statistics for comparison.
5000). All were males, with 78 (89.7%) of them being unmarried. While 44 (50.6%) were students, and 11 (12.6%) were working, the remaining 32 (36.8%) were unemployed. The religious affiliations were: Hindu 65 (74.7%), Sikh 17 (19.5%), and others 5 (5.7%). The family types were: nuclear 68 (78.2%), extended 11 (12.6%) and joint 8 (9.2%). Social support was assessed as fair to good in 51 (58.6%) (fair in 46, 52.9%) and minimal to poor in 36 (41.3%) (minimal in 35, 40.2%) subjects. Urban subjects were in majority 69 (79.3%), with 56 (64.4%) of them residing within 40 km of the DDTC. Most of the subjects were brought by their family members 70 (80.5%); only a few had come on their own 5 (5.7%). Demographic data of missing records (N=5) and available case records (N=87) were comparable in gross terms; small number of missing records precluded the application of inferential statistics for comparison.
Clinical profile: At initial presentation, of the 74 (85.1%) cases who met the ICD-10 criteria for substance dependence, 66 (75.9%) were actively inhaling, whereas eight (9.2%) were abstinent. Of the remaining 13 (14.9%) cases, only three (3.4%) cases met the ICD-10 criteria for harmful use, while 10 (11.5%) reported only use that did not meet the criteria for substance use disorder. The main substance of concern for the subjects or their family members was inhalant in 41 (47.1%), opioids in 23 (26.4%) and cannabis in 11 (12.6%) cases and alcohol and nicotine in 6 (6.9%) each.
The inhalants used were: typewriter correction fluid in 64 (73.6%), typewriter diluent fluids in 17 (19.5%), and glue/adhesives in six (6.9%) cases. The reported reasons for inhalant use were curiosity in 54 (62.1%), peer pressure in 31 (35.6%), and source of alleviating frustration in 2 (2.3%) cases.
The mean ± SD ages were: first use of inhalants at 16.31 ± 4.22 yr (range: 5-30 yr) and onset of inhalant dependence at 16.75±3.99 yr (range: 7-30 yr). The family history of substance dependence was present in 26 (32.9%) subjects.
Co-morbidity: The substances other than inhalants used in these cases were tobacco in 66 (75.9%), alcohol in 33 (37.9%), cannabis in 32 (36.8%), opioids in 31 (35.6%), benzodiazepines in five (5.7%) and carisoprodol in one (1.1%) cases.
Psychiatric co-morbidity present in 23 (26.4%) subjects was accounted for by psychosis in eight, conduct disorder in six, bipolar disorder and personality disorder in three each, and generalized anxiety disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and mental retardation in one case each. Other diagnosis was epilepsy in one case.
Other clinical characteristics: At initial interview, motivation was found poor in 12 (13.8%), poor to superficial in 15 (17.2%), superficial in 38 (43.7%), superficial to fair in 15 (17.2%), and fair or good in seven (8.0%) cases, respectively. High risk behaviours in the form of injecting drug use and high risk sexual behaviour were present in four (4.6%) and five (5.7%) subjects, respectively.
Drug related harms were present in at least one of the domains in a majority of the cases. The worst affected domains were family (94.3% cases), social (85.1% cases), health (88.2%), finance (69%) and occupation (47.1%); and least affected domains were marital (10.3%), and legal (25.3%). When present, the harm was mostly mild or moderate for the family (74.4 and 19.5%, respectively), social (59.8 and 23%, respectively), and health domains (57.5 and 17.2%, respectively); and moderate or severe for occupation (26.5 and 17.2%, respectively), and finance domains (26.4 and 23%, respectively).
Follow up and outcome: Of the 87 subjects, 17 (19.5%) never reported for a follow up. The follow up duration was for 4.48±9.00 months (median 2 months; range 0-60 months). This follow up included 4.45 ± 6.31 hospital visits (median 3; range 0-36). Of those who reported for a follow up at least once (N=70), their last follow up had recorded the outcome as abstinence in 47 (54%) cases, continued use of inhalants without any period of abstinence in 20 (23%) subjects, and relapse to inhalant use in 3 (3.5%) subjects.
Subjects who were followed up had significantly higher family income (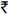 8620.29 + 7624.74 per month vs
8620.29 + 7624.74 per month vs 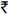 4055.56 + 4768.31 per month, P<0.05), started substance use out of curiosity (P <0.05), and were more impaired in family and social domains compared to those who were not followed up.
4055.56 + 4768.31 per month, P<0.05), started substance use out of curiosity (P <0.05), and were more impaired in family and social domains compared to those who were not followed up.
Subjects with improved/abstinent status at the last follow up were from joint families, had more commonly started substance use out of curiosity (P<0.05), substances other than inhalants being the primary substance of use (P<0.01), higher impairment in health (P <0.05) and occupation domains.
Simple binary logistic regression analysis showed that significant predictors for subjects following up were having lower social support, and substances other than inhalants being the primary substance of use. Significant predictors for abstinence at follow up were having substances other than volatile solvents being the primary substance of use and curiosity as the reason for initiation of substance use.
Discussion
In the West, inhalant abuse has been documented for almost two centuries5. In India, inhalant abuse emerged only a few decades back but has shown a rapid increase, especially among the urban youth7. In our study, the inhalants included typewriter correction fluid, diluents, and glues which are available easily and at a relatively low cost. Being low cost stationery items used in schools and offices, and being easily available to children, correction fluid has been reported to be the commonest inhalant abused in India71415. In other countries, the more frequently abused inhalants are solvents and glues; adhesives with toluene being the main solvent used246.
All inhalant users in our study were males, mostly from urban and middle socio-economic class, and tobacco co-users; a profile similar to that reported from India as well as abroad34567. Our all-male sample could be due to either a very low female-prevalence or a higher social stigma for substance abuse among the females, especially for those seeking treatment. This gender profile conformed to the rarity of treatment seeking female substance abusers at our centre, in our region and in India2930, but was in contrast to similar lifetime prevalence rates for girls and boys (8.8 and 8.7%, respectively) in the United States59. The mean age at the onset of inhalant use was similar to other studies from India and from the west45891421.
In our study the cases were brought to the clinic by the family members and more than half of them had fair to moderate social support. This was in contrast to poor social support being reported by others from India16171819. Three-fourth of our subjects reported abuse of more than one substance. Inhalant abuse has been shown as a predictor of future poly-substance abuse514172132.
The results of our study must be considered with its limitations. It focused only on treatment seekers; hence the results may not be a true representation of inhalant abusers in the community. It was a retrospective chart review; hence data may not be completely accurate. A retrospective recall bias leading to incorrect reporting of age of onset of use and dependence is likely. Also, the modules used to assess social support, impairment and motivation, were centre specific and not tested for reliability.
In conclusion, our study depicted that around three-fourth of the subjects abused more than one substance. Subjects whose primary substance of abuse was inhalants were less likely to follow up and being abstinent at follow up. In addition, inhalants users develop marked impairment in functioning in multiple domains. Thus, IUD needs to be recognized as a public health problem in India that needs specific interventions. Early intervention starting at the primary school level might help to a significant degree in reducing the burden of dependence later on. Adequate training needs be imparted to the clinicians to develop skills to identify and treat IUDs. Also, more research needs to be done to identify the extent of the problem in the country and to devise effective preventive and treatment modules for IUD.
References
- Marijuana, Hallucinogens, and club drugs. In: Frances RJ, Miller SI, Mack AH, eds. Clinical textbook of addictive disorders (3rd ed). New York: The Guildford Press; 2005. p. :175-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance and other drug abuse inhalation in Spain. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:931-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse among street children in Upper Egypt. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):35-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse in Mexico: correlates and trends. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):40-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse in the United States. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):8-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse among high school students in South America. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):27-34.
- [Google Scholar]
- Demographic and social characteristics of solvent abuse patients in Japan. Am J Addict. 1994;3:165-76.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse among youth in Israel: results of a national school survey. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):21-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant use initiation among U.S. adolescents: evidence from the national survey of parents and youth using discrete-time survival analysis. Addict Behav. 2011;36:878-81.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant abuse: a study from a tertiary care de-addiction clinic. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2011;21:157-63.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant use among street children in Delhi: A situation assessment (Report no.SE/08/094199) New Delhi: National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre, All India Institute of Medical Sciences; 2009.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant abuse: a growing public health concern in India. Addiction. 2003;98:1169-72.
- [Google Scholar]
- Drug abuse among street children in Bangalore. Available from: http://www.nimhans.kar.nic.in/cam/CAM/Drug_Abuse_Street_Children_Bangalore.pdf
- [Google Scholar]
- Phenomenology of gasoline intoxication and withdrawal symptoms among adolescents in India: A case series. Am J Addict. 1999;8:254-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant abuse (typewriter correction fluid) in street children. J Addict Med. 2008;2:175-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Volatile substance misuse among street children in India: a preliminary report. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):46-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Street and working children of Delhi, India, misusing toluene: an ethnographic exploration. Subst Use Misuse. 2005;40:1659-79.
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhalant abuse by adolescents: a new challenge for Indian physicians. Indian J Med Sci. 2004;58:245-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime for South Asia Regional Office for South Asia (UNODC ROSA). Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MSJE), Government of India. In: The extent, pattern and trends of drug abuse in India: National survey. New Delhi: UNODC ROSA, MSJE; 2004.
- [Google Scholar]
- The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. (10th ed). Geneva: WHO; 1992.
- [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MSJE), Government of India and United Nations International Control Programme Drug, Regional Office for South Asia UNDCPROSA. In: Women and drug abuse. The problem in India. New Delhi: MSJE and UNDC-ROSA; 2002.
- [Google Scholar]
- Substance-dependent women attending a de-addiction center in North India: sociodemographic and clinical profile. Indian J Med Sci. 2005;59:283-91.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chronic toluene misuse among roma youth in Eastern Slovakia. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):57-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- The epidemiology of volatile substance misuse among school children in Bogota, Colombia. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(Suppl 1):50-6.
- [Google Scholar]






