Translate this page into:
Predictive power of tumour budding for lymph node metastasis in colorectal carcinomas: A retrospective study
For correspondence: Dr Brototo Deb, 30 Mondal Para Road Joypur Behala, Kolkata 700 034, West Bengal, India e-mail: brototo.deb@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
Tumour budding is a feature of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation that is characterized histologically within the tumour stroma by the presence of isolated cells or clusters of less than five cells which are different from the other malignant cells. This could be present around the invasive margin of the tumour, called peritumoural budding, or in the bulk of the tumour, called intratumoural budding. The aim of this study was to assess the predictive power of tumour budding for lymph node metastasis and its relationship with other features of tumour progression in colorectal carcinoma (CRC).
Methods:
Preoperative colonoscopic biopsies and consecutive resection specimens from 80 patients of colorectal cancer were taken. In the biopsy, intratumoural budding was looked for and graded. In the resection, peritumoural budding was seen and graded along with other features such as grade of the tumour, lymphovascular emboli and tumour border configuration.
Results:
Intratumoural budding was seen in 23 per cent (18/80) and peritumoural in 52 per cent (42/80) of cases. Intratumoural budding was associated with the presence of lymphovascular emboli (P=0.002) and irregular tumour border configuration (P=0.004). Peritumoural budding was also significantly associated with the presence of lymphovascular emboli and irregular margins (P<0.001). Both intra- and peritumoural budding were not associated with the grade of the tumour. Both intra- and peritumoural budding had a significant association with lymph node metastasis (LNM) (P<0.001).
Interpretation & conclusions:
Our findings indicate that tumour budding in preoperative biopsy and resection specimens may predict a possibility of finding LNM in patients with CRC.
Keywords
Colorectal carcinoma
intratumoural budding
lymph node metastasis
lymphovascular emboli
peritumoural budding
tumour budding
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is one of the most common cancers leading to a considerable amount of cancer-related mortality and morbidity. The grading and staging of CRC done by the TNM (tumour-node-metastasis) system given by the American Joint Committee on Cancer is not always accurate in its predictions1. Hence, there is always a need for identification of other prognostic biomarkers, one of which is the presence of tumour budding. Tumour budding takes place after an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation2 by which cells gain increased migratory capacity and invasiveness3, ultrastructurally characterized by loss of basement membrane and poorly developed or absent desmosomes or junctional complexes4.
In routine staining, peritumoural buds look like isolated undifferentiated tumour cells or in clusters containing less than five cells separated from the main tumour at the invasive margin. Such buds when present within the main tumour mass are known as intratumoural budding. Usually, CRC is diagnosed by taking a colonoscopic biopsy from the superficial areas of the tumour. This is sufficient to diagnose the disease but not the stage, as it does not reach the invasive margin of the tumour. However, the preoperative biopsy can still be used to prognosticate the disease by looking for intratumoural budding. Postoperatively, peritumoural buds can be seen in the excised specimen when the tumour margins are sampled5. Tumour budding is described as a strong predictor of lymph node involvement, lymphatic invasion, metastases, local recurrences and thereby poor disease-free survival67. This study was undertaken to evaluate the predictive power of tumour budding lymph node involvement, metastasis, and its relation with other features of tumour progression in CRC.
Material & Methods
The study was conducted in the department of Pathology of Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research, Puducherry, India, in May and June 2015 after obtaining approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee. It was a cross-sectional retrospective analysis of 80 samples (40 nodes positive and 40 nodes negative) of CRCs diagnosed for a two and half year period from January 2013 on preoperative colonic biopsies with consecutive colonic resection specimens and not undergone neoadjuvant chemotherapy (inclusion criteria). In cases where relevant slides/blocks were not available, were excluded.
Olympus CX41 microscope (Olympus Medical Systems India Pvt Ltd., Gurgaon) was used with a field diameter of 2.2 mm for tumour grading. Tumour was graded as well/moderate/poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas. The tumour margin was assessed as irregular or expanding/regular (Fig. 1A & B). The presence of lymphovascular emboli (Fig. 1C) was noted. Tumour budding was looked for in the area of maximal intensity and its grading was done. More than 10 clusters of cells consisting of less than five cells in ×20 objectives were taken as high-grade tumour budding8. The preoperative colonic biopsies were studied for intratumoural budding. The consecutive resection specimens were also searched for peritumoural budding, and the presence or absence of metastasis in lymph nodes (10-12 samples per patient). Tumour buds were picked up from routine haematoxylin and eosin (H and E) staining of samples.
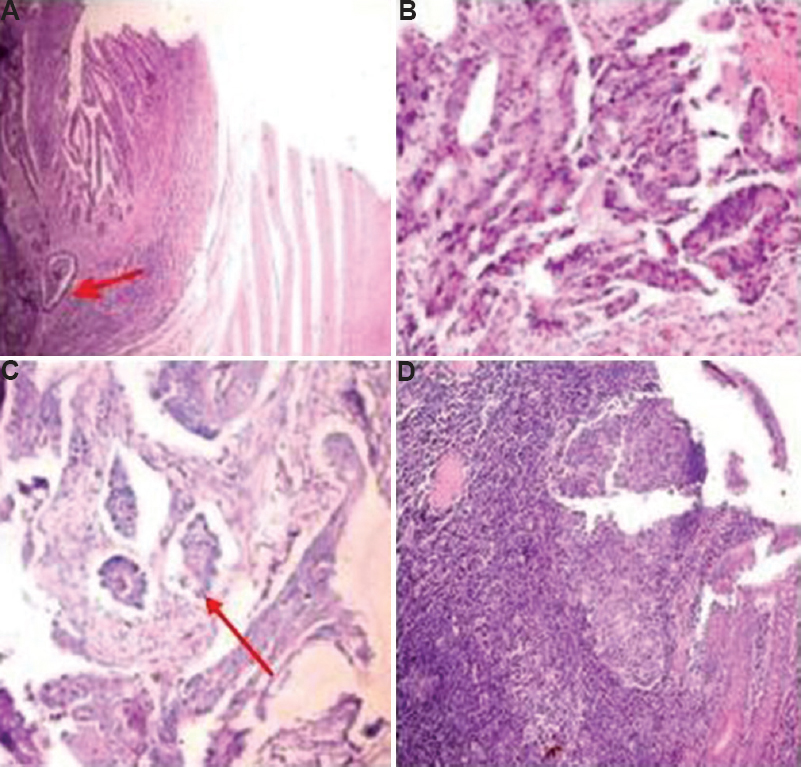
- Adenocarcinoma with (A) regular borders (red arrow depicting the border) (B), with irregular borders (C), with lymphovascular emboli (red arrow depicting emboli) (H and E, ×100), and (D) dense inflammation around tumour making identification of tumour buds difficult (H and E, ×200).
Statistical analysis was done using the Chi-square test. Risk factors which were significant (P<0.005) in the univariate analysis, were included in subsequent multivariate binomial regression analysis using the backward Wald method9. Selection of the logistic models was based on Nagelkerke's R2, the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and the receiver operating characteristic curve9.
Results & Discussion
Of the 80 patients with CRC, 43 (54%) were male. The age ranged from 20 to 86 yr with 59 per cent falling in the age group of 50-69 yr. Intratumoural budding (Fig. 2A) was found in 23 per cent (18/80) and peritumoural budding (Fig. 2B) in 52 per cent (42/80) of cases. High-grade budding was observed in one intratumoural bud and four peritumoural buds.
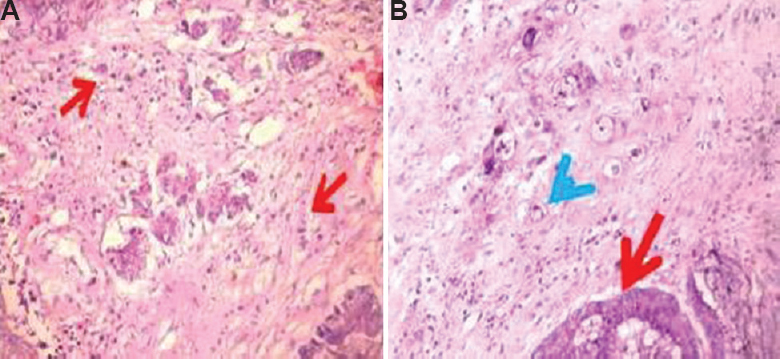
- Intratumoural buds (A) (H and E, ×200) (red arrows depict the abnormal cells), and (B) peritumoural buds (H and E, ×400) (red arrow depicts tumour and blue arrow shows peritumoural buds).
The association of both intra- and peritumoural budding with lymph node metastasis (LNM) was found to be significant (P<0.05). The sensitivity and specificity of intratumoural budding for LNM were 40 and 95 per cent, respectively, with a positive predictive value of 89 per cent while the same in case of peritumoural budding were 93, 88 and 88 per cent, respectively. Both intra- and peritumoural budding were associated with the presence of lymphovascular emboli and irregular tumour border configuration (P<0.05) (Table I). A logistic regression was performed to ascertain the predictability of lymph node status from the other independent parameters such as the presence of intratumoural, peritumoural budding, lymphovascular emboli and irregular tumour margins. Grade was not included because it was found to be insignificant in univariate analysis. The logistic regression model was found to be insignificant. The model explained 71.2 per cent (Nagelkerke's R2) of the variance in lymph node status and correctly classified 90 per cent (Table II) of the cases. On multivariate analysis, only the presence of peritumoural budding was significantly associated with lymph node status. The presence of peritumoural budding was 9.3 times more likely to show lymph node positivity in the following lymph node biopsy (Table III).
| Parameter | Intratumoural budding | Peritumoural budding | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n=18) | Negative (n=62) | P | Positive (n=42) | Negative (n=38) | P | |
| LN status | ||||||
| Positive (n=40) | 16 | 24 | <0.001 | 37 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Negative (n=40) | 2 | 38 | 5 | 35 | ||
| LVE | ||||||
| Positive (n=32) | 13 | 19 | 0.002 | 26 | 6 | <0.001 |
| Negative (n=48) | 5 | 43 | 16 | 32 | ||
| Margins | ||||||
| Irregular (n=61) | 17 | 44 | 0.004 | 41 | 20 | <0.001 |
| Regular (n=19) | 1 | 18 | 1 | 18 | ||
| Grade | ||||||
| MOD (n=25) | 8 | 17 | 0.247 | 16 | 9 | 0.228 |
| WELL (n=55) | 10 | 45 | 26 | 29 | ||
MOD, moderately differentiated; WELL, well differentiated; LVE, lymphovascular emboli; LN, lymph node
| Observed status | Predicted status | Positive/negative predictive value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lymph nodes negative (n=38) | Lymph nodes positive (n=42) | ||
| Lymph nodes negative (n=40) | 35 | 5 | 87.5 |
| Lymph nodes positive (n=40) | 3 | 37 | 92.5 |
| Overall percentage | 90 | ||
| Presence of | Prevalence rate ratio (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|
| Peritumoural budding | 9.30 | 0.002 |
| Intratumoural budding | 0.96 | 0.726 |
| LVE | 1.25 | 0.159 |
| Tumour margins | 1.13 | 0.837 |
CI, confidence interval
Tumour budding as observed at the invasive tumour front and also within the main tumour mass is considered as an early step in tumour invasion and metastasis. Studies have confirmed its presence to be an independent adverse prognostic factor in CRC10. If the preoperative biopsy samples of CRC patients had high intratumoural budding, chances for the resection specimen to show high peritumoural budding and LNM were more5. Tumour budding not only is a predictor of spread but also helps in risk stratification of CRCs. With increase in the number of early CRC where local excision is curative in the absence of LNM, proper identification of predictors of LNM is important in decision-making of further management following local therapy. Tumour budding in submucosally invasive carcinomas is also an independent prognostic factor, thereby helping to identify a subset of high-risk patients requiring segmental resection11. The mere presence or absence of tumour buds121314 strongly predicts LNM in submucosal invasive carcinomas. A meta-analysis by Beaton et al15 has also suggested it as a predictor of LNM in early CRCs. It can be a strong independent predictor of LNM (relative risk: 5.1, 95% confidence interval: 3.6-7.3)16. In the study by Giger et al5, in biopsy specimens, high intratumoural budding was seen in 17 per cent, whereas sparse tumour budding, detectable only at high-power magnification, was seen in 83 per cent samples. In our study, low grade intratumoural budding was detected in 23 per cent of cases. The reason could be the difficulty in spotting the highly packed tumour buds within the bulk of the tumour at low power. This may also probably be because the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition takes place from the basal to the apical tumour cells. Hence, peritumoural budding would occur earlier than intratumoural budding.
This was a pilot study which showed that tumour budding was associated with LNM and aggressive morphological features of tumour such as the presence of lymphovascular emboli and invasive tumour border configuration. Interobserver differences may be present in noting tumour budding. Another significant problem is that it sometimes gets mixed with the inflammatory cells in local tissue reaction (Fig. 1D). This problem can be circumvented using immunohistochemical (IHC) methods which make the buds stand out. The tumour buds should not be confused with apoptotic bodies and cellular debris which might get stained by pan-cytokeratin IHC17.
An important limitation of this study was lack of information regarding the stage of the tumour. Being a retrospective study, it was not possible. Assessment of the mere presence or absence of tumour buds has been found to be effective in predicting LNM, thereby removing the complexities of the various grading systems12. As the presence of tumour budding can be used as a predictor of aggressive nature, risk stratification of patients can be attempted based on its presence or absence. The International Tumour Budding Consensus Conference (ITBCC) 201617 has recommended tumour budding as a predictor of LNM and survival in pT1 and stage II CRCs, respectively. They recommend counting of tumour buds by H and E in a hotspot (a field measuring 0.785 mm2) at the invasive front. Ten separate fields at the invasive front are to be scanned to select the hot spot. A conversion table has also been provided to standardize the bud count for different microscopes. The ITBCC suggested a three-tier system classifying buds into low (0-4)/intermediate (5-9)/high (10 or more) for risk stratification17. Hence, by establishing tumour budding in preoperative biopsy and resection samples, it would be possible to predict presence of LNM in CRC patients.
Financial support & sponsorship: The first author (BD) acknowledges the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, for providing Short Term Studentship (ICMR STS No. 2015-01499; Institutional Ethics Committee certificate number: JIP/IEC/15/2015/736)
Conflicts of Interest: None.
References
- TNM staging system of colorectal carcinoma: A critical appraisal of challenging issues. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:837-52.
- [Google Scholar]
- Epithelial mesenchymal transition and tumor budding in aggressive colorectal cancer: Tumor budding as oncotarget. Oncotarget. 2010;1:651-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tumor budding in colorectal carcinoma: Time to take notice. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1315-25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Intra-tumoral budding in preoperative biopsy specimens predicts lymph node and distant metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1048-53.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of the usefulness of tumor budding on the prediction of metastasis to the lung and liver after curative excision of colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52:1432-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Budding is useful to select high-risk patients in stage II well-differentiated or moderately differentiated colon adenocarcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003;46:1400-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tumour ‘budding’ as an index to estimate the potential of aggressiveness in rectal cancer. Histopathology. 2002;40:127-32.
- [Google Scholar]
- A prediction model for spontaneous regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2, based on simple clinical parameters. Hum Pathol. 2017;59:62-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tumor budding in colorectal cancer-ready for diagnostic practice? Hum Pathol. 2016;47:4-19.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tumour budding at the deepest invasive margin correlates with lymph node metastasis in submucosal colorectal cancer detected by anticytokeratin antibody CAM5.2. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:293-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Novel predictors for lymph node metastasis in submucosal invasive colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5936-44.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tumor budding as a risk factor for nodal metastasis in pT1 colorectal cancers: A meta-analysis. Hum Pathol. 2017;65:62-70.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pathological prognostic factors predicting lymph node metastasis in submucosal invasive (T1) colorectal carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:1068-72.
- [Google Scholar]
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of histopathological factors influencing the risk of lymph node metastasis in early colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2013;15:788-97.
- [Google Scholar]
- Predicting lymph node metastasis in pT1 colorectal cancer: A systematic review of risk factors providing rationale for therapy decisions. Endoscopy. 2013;45:827-34.
- [Google Scholar]
- Recommendations for reporting tumor budding in colorectal cancer based on the International Tumor Budding Consensus Conference (ITBCC) 2016. Mod Pathol. 2017;30:1299-311.
- [Google Scholar]






