Translate this page into:
Oro-facial digital syndrome (type II) with lingual lipomas
* For correspondence: rizdent@yahoo.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A one and a half year old boy presented to the department of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology in Yenepoya Dental College Hospital, Mangaluru, India, in April 2014, with a complaint of swelling on either side of tongue and partial tongue tie. Family history revealed that he was born at term (normal vaginal delivery) out of a consanguineous marriage of 3rd degree. No systemic abnormalities were reported. On clinical examination, apart from the delayed eruption, orbital and oral deformities included hypertelorism, telecanthus, strabismus, ankyloglossia, partial cleft of upper lip (vermilion border region) and two solitary tongue nodules on either side of the anterolateral border of the tongue. The nodules were movable, round masses of 1×1 cm size, cream coloured and soft in consistency (Fig. 1). Digital deformities included post-axial polydactyly involving both upper (Fig. 2) and lower extremities (Fig. 3). The tongue nodules were diagnosed as lipoma using haematoxylin and eosin and confirmed by S-100 immunopositivity (Figs 4 & 5). The combination of hypertelorism, cleft lip, tongue nodules and polydactyly indicated towards the features of orofacial digital syndrome (type II). Lipomas were surgically excised; ankyloglossia released and the patient was called for follow up visit once in every three months. However, the patient was lost to follow up.
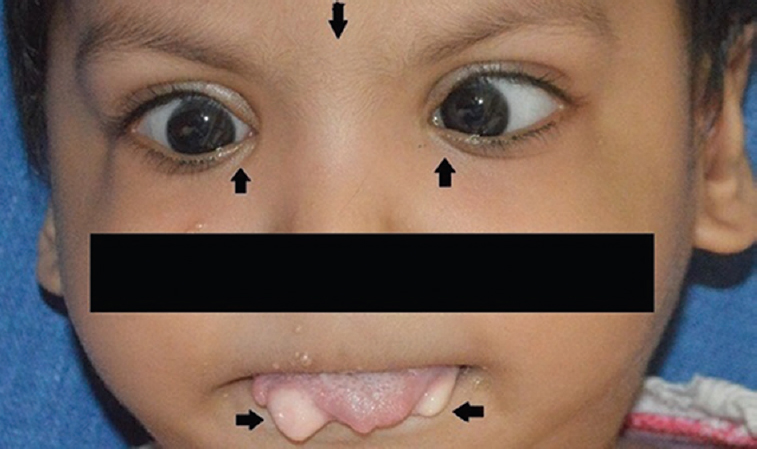
- Orbital deformities including hypertelorism, telecanthus and strabismus and lingual lipomas (arrows).

- Polydactyly (arrows) involving both hands.
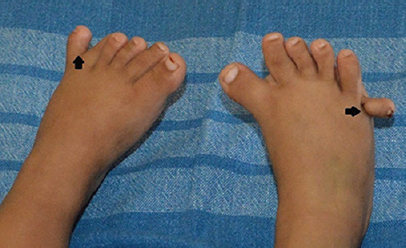
- Polydactyly (arrows) involving both feet.
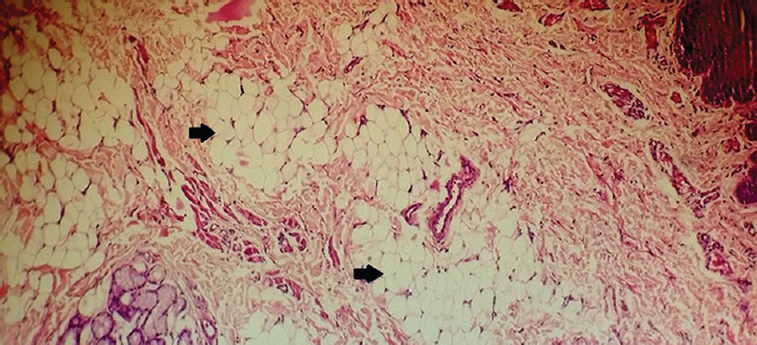
- Section showing collection of mature fat cells separated by fibrous septa (arrows) (H & E, ×40).
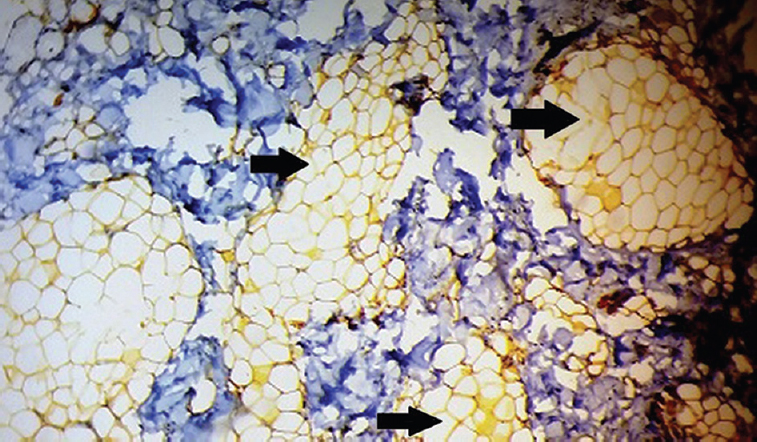
- Section showing S-100 immunopositive adipose cells (×40). Arrows show S-100 immuno-positive adipose cells.





