Translate this page into:
Evaluation of first information reports of Delhi police for injury surveillance: Data extraction tool development & validation
For correspondence: Dr Sajjan Singh Yadav, House No. 1, Vinay Marg, Chanakya Puri, New Delhi 110 021, India e-mail: sajjan.yadav@lshtm.ac.uk
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
Policymakers and health professionals need to know the distribution, patterns, trends and risk factors of injury occurrence to develop strategies that reduce the incidence of injuries. The first information report (FIR) of Indian police is one potential source of this information. The aims of this study were to identify the minimum data set (MDS) recommended for injury surveillance, to develop a tool for data extraction from FIRs, to evaluate whether FIRs contain this MDS and to assess the inter-rater reliability of the tool.
Methods:
This was a cross-sectional study of incidents reported to Delhi Police in 2017. A systematic literature search was conducted to identify the MDS recommended for injury surveillance. A tool was designed for extraction of data, and its inter-rater reliability was assessed using Cohen's kappa and the percentage availability of each MDS data item in the FIRs, was calculated.
Results:
The literature review identified 24 reports that recommended 12 MDS for injury surveillance. The FIRs contained complete information on the following five MDS: sex/gender (100%), date of injury (100%), time of injury (100%), place of injurious event (100%) and intent (100%). For the following seven MDS, information was not complete: name (93.1%), age (67.2%), occupation (32.8%), residence (86.2%), activity of the injured person (86.2%), cause of the injury (93.1%) and nature of the injury (41.4%). The inter-rater reliability of the data extraction tool was found to be almost perfect.
Interpretation & conclusions:
Information on injuries can be reliably extracted from FIRs. Although FIRs do not always contain complete information on the MDS, if missing data are imputed, these could form the basis of an injury surveillance system. However, use of FIRs for injury surveillance could be limited by the representativeness of injuries ascertained by FIRs to the population. FIRs thus have the potential to become an important component of an integrated injury surveillance system.
Keywords
First information reports
injury surveillance
inter-rater reliability
minimum data sets
police records
Unintentional injuries kill more than five million people each year globally and cause several millions to live with disability1. Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) report 90 per cent of global injury-related deaths2. Injury is an important contributor to disease burden in India and is one of the leading causes of death for all ages34. Injuries have a definitive causative pattern and mechanism and thus are both predictable and preventable3. Policymakers and public health professionals need to know the distribution, patterns, trends and risk factors of injury occurrence. These data can help in developing public health strategies that reduce the incidence of injuries5. An injury surveillance system can provide these data367.
Injury surveillance systems are often based on hospital records89. Such surveillance systems tend not to ascertain all injury events and may be biased towards more severe injuries710. Hospital attendance for non-fatal injuries is low, especially in LMICs; documentation of injuries is generally poor and information about the circumstances of injury is often lacking711. Studies from India report that some non-fatal and minor road traffic injuries and fatalities occurring after a crash go unreported12. Police records can be considered as one of the potential data sources for injury surveillance6712. In India, the information received by the police pertaining to a crime, including an accident, is to be recorded in a prescribed format, known as the first information report (FIR)13. The FIRs could be a potential data source for an injury surveillance system14. This study was undertaken to identify the minimum data set (MDS) recommended for injury surveillance, to develop a tool for the extraction of MDS data from FIRs, to evaluate whether FIRs contain this MDS and to assess the inter-rater reliability of the data extraction tool.
Material & Methods
This was a cross-sectional study conducted in Delhi, India, and was based on FIRs of accidents registered from January 1 to December 31, 2017. Injuries included in this study did not include psychological harms. A list of all accident FIRs was obtained from Delhi police, and FIR documents were downloaded from the Delhi Police website15.
This study was approved by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), London, UK, Observational Research Ethics Committee vide LSHTM Ethics Reference number 15992 dated November 26, 2018.
Data extraction tool development: A systematic search of the published and grey literature was conducted to identify MDS recommended for injury surveillance. A tool was designed for the extraction of data from FIRs. Standard classifications and codes recommended by the WHO and other international guidelines were used in the tool1617. The tool was reviewed by two injury experts and then by three professionals, each qualified at least as Masters in Public Health18. In a third round of development, the tool was applied by four data extractors who were subsequently invited for a focus group discussion. A set of instructions for data extractors when using the tool was also prepared.
Sample size and sampling: A random sample of 50 FIRs was selected from all 8638 FIRs pertaining to accidents reported in Delhi in 2017: all the 8638 FIRs were serially numbered. A list of 50 random numbers in the range of 1 to 8638 was generated from the website random.org. FIRs having serial numbers corresponding to these random numbers were selected for inclusion in the study. The sample size for the inter-rater reliability study was based on published recommendations192021. A sample size of 50 was sufficient to allow us to estimate the percentage availability of data items with reasonable precision (i.e. within 13% of the true percentage with 95% confidence). Data were extracted from 50 FIRs using the data extraction tool. The percentage availability for each MDS data item with respect to each of the 58 persons reported with injuries in these 50 FIRs was calculated.
Estimation of inter-rater reliability: To assess inter-rater reliability, data extraction was first conducted by the lead author and then by one of the professionals who had tested the tool. Cohen's kappa coefficient (κ) was calculated as the measure of inter-rater reliability2223. Cohen's kappa gives a quantitative measure of the magnitude of agreement between observers after taking into account any agreement due to chance alone. Cohen's kappa was calculated using the following formula23:
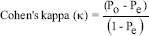
Where, Po=Proportion of observed agreement; Pe=Proportion of agreement by chance alone.
The kappa values ranged from −1 to 1, where 1 is perfect agreement and 0 is no agreement beyond what would be expected by chance. Kappa values <0 indicated no agreement or poor agreement24. We interpreted the estimates of Cohen's kappa using the standard for strength of agreement provided by Landis and Koch24. Accordingly, a kappa value of 0 indicates poor agreement; 0.01-0.20 indicates slight agreement 0.21-0.40 indicates fair agreement; 0.41-0.60 indicates moderate agreement; 0.61-0.80 indicates substantial agreement and 0.81-1.0 indicates almost perfect agreement19. After obtaining the values of kappa, its precision was quantified by calculating 95 per cent confidence intervals for each kappa value23.
Results
Dataset requirements for an injury surveillance system: The literature search yielded 24 studies including 13 national and international guidelines and data standards. These included three sets of WHO guidelines61725. The WHO guidelines recommend the following eight data items which must be collected for injury surveillance: (i) person identifier, (ii) age of the injured person, (iii) sex of the injured person, (iv) intent, (v) place of injury, (vi) nature of activity when the injury happened, (vii) cause of injury, and (viii) nature of injury61725. These eight data items were included as the MDS in our tool. In addition, if a data item was recommended as an MDS data item by the majority of the remaining 10 guidelines, it was also included in the tool10262728293031323334. This yielded four further data items namely (ix) date of injury, (x) time of injury, (xi) occupation of the injured person, and (xii) residence of the injured person.
Development of the data extraction tool: Based on the recommendations of the two international injury experts, local terms used in the tool were replaced with internationally accepted ones. The recommendations of the three professionals in public health led to reorganization of some questions and to simplification of the language of some questions. Subsequent testing of the tool by four data extractors led to further improvements: questions that were unclear were modified. More response codes were added to some questions, for example, a response code 100 was added to indicate that a question was not relevant. The inter-rater reliability of the tool was estimated: kappa values for agreement for extraction of the MDS items between the two raters were found to be between 0.40 and 1.0, indicating between substantial and almost perfect agreement. Subsequent focus group discussion with the four data extractors highlighted a lack of clarity between some response options, too many response options for some questions, choice of multiple possible response options for a few questions and a lack of information about the type of health facility and legal status of colony as reasons for low agreement. These issues were addressed in the revised tool.
Availability of information on minimum data set: Data extracted from the random sample of 50 FIRs indicated that a total of 58 persons were injured in these 50 incidents reported to the Delhi Police. Results on the percentage availability of information on the 12 MDS items with respect to these 58 victims are presented in Table I. The FIRs contained complete information on 5 of the 12 MDS items namely sex/gender, date, time, place and intent. For the following four items, information was above 80 per cent complete: name (93.1%), residence (86.2%), cause of injury (93.1%) and activity (86.2%) of the injured person; for the following three items, information was above 30 per cent complete: age (67.2%), occupation (32.8%) and nature of the injury (41.4%).
| Data item | Number of injured persons for which information was available | Percentage availability |
|---|---|---|
| Unique identification/name of the injured person | 54 | 93.1 |
| Age | 39 | 67.2 |
| Sex/gender | 58 | 100 |
| Occupation | 19 | 32.8 |
| Residence | 50 | 86.2 |
| Date of injury | 58 | 100 |
| Time of injury | 58 | 100 |
| Place of injurious event | 58 | 100 |
| Intent | 58 | 100 |
| Mechanism/external cause of injury | 54 | 93.1 |
| Nature of injury | 24 | 41.4 |
| Nature of activity | 40 | 86.2 |
The percentage availability of data varied between fatal and non-fatal injuries. Of the variables for which information was not complete, the percentage availability of data was higher in cases of fatal injuries for age, occupation, mechanism/external cause of injury, nature of injury and nature of activity (Table II). The percentage availability of data was higher for non-fatal injuries in case of unique identification and residence of victim (Table II). The differences in the percentage availability of data between fatal and non-fatal injuries are shown in Table II.
| Data item | Injuries reported in 50 FIRs | Information found available in FIRs | Percentage availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatal | Non-fatal | Fatal | Non-fatal | Fatal | Non-Fatal | |
| Unique identification | 3 | 55 | 1 | 53 | 33.3 | 96.4 |
| Age | 3 | 55 | 3 | 36 | 100 | 65.5 |
| Sex/gender | 3 | 55 | 3 | 55 | 100 | 100 |
| Occupation | 3 | 55 | 2 | 17 | 66.7 | 30.9 |
| Residence | 3 | 55 | 1 | 49 | 33.3 | 89.1 |
| Date of injury | 3 | 55 | 3 | 55 | 100 | 100 |
| Time of injury | 3 | 55 | 3 | 55 | 100 | 100 |
| Place of injurious event | 3 | 55 | 3 | 55 | 100 | 100 |
| Intent | 3 | 55 | 3 | 55 | 100 | 0 |
| Mechanism/external cause of injury | 3 | 55 | 3 | 51 | 100 | 92.7 |
| Nature of injury | 3 | 55 | 3 | 21 | 100 | 38.2 |
| Nature of activity | 3 | 55 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 90.9 |
FIRs, first information reports
Inter-rater reliability: Cohen's kappa values were found to range between 0.87 and 1, indicating almost perfect agreement between the two data extractors when extracting data for the MDS. The kappa coefficients calculated for the MDS data items along with a number of response options in the tool, standard errors and 95 per cent confidence intervals are presented in Table III.
| Data item | Number of injured persons | Number of response options in the data extraction tool | Cohen’s kappa value | SE | 95% CIs for the kappa estimates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unique identification | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Age | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Sex/gender | 58 | 3 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Occupation | 58 | 19 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Residence | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Date of injury | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Time of injury | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Place of injurious event | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Intent | 58 | 2 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Mechanism/external cause of injury | 58 | 15 | 0.87 | 0.01 | 0.86-0.88 |
| Nature of injury (non-fatal) | 58 | 19 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Nature of injury (fatal) | 58 | 19 | 1 | 0.00 | 1 |
| Nature of activity (non-fatal injury) | 58 | 18 | 0.97 | 0.02 | 0.80-0.98 |
| Nature of activity (fatal injury) | 58 | 18 | 0.97 | 0.02 | 0.95-0.99 |
CIs, confidence intervals; SE, standard error
Discussion
Twelve data items were identified which formed the MDS for injury surveillance. The FIRs were found to contain complete information on five of the 12 MDS data items. For seven MDS items, information was less complete. Missingness of data was substantial (i.e. >10%) for five data items and slight for two data items35.
The reliability of data extraction from the FIRs as assessed using Cohen's kappa was found to be almost perfect. Studies from other countries have reported on the completeness of police records as a source of data on road traffic and other injuries, but none of those have evaluated the suitability of police records for an injury surveillance system3637. No study has so far reported on the use of police records to ascertain construction-site injuries. The systematic extraction of data from police records using a data extraction tool and an assessment of the tool's reliability were done in the present study. In India, where data on injuries are not routinely published, this study opens a new area of research on injury epidemiology. The use of Cohen's kappa for estimating inter-rater agreement, requires certain conditions to be met: cases rated must be independent of each other, the raters must work independently of each other, rating categories must be mutually exclusive and exhaustive, the sample of cases used in the reliability data should be a random sample and the data extractors used for inter-rater reliability are not persons who are difficult to find35. All these conditions were met in this study.
One limitation of the study lied in the inherent problem of police records as a source of injury information including under reporting, low reliability, bias towards fatal and severe injuries and recording of information without going into the veracity of claims7. Another limitation of the study was that the data extraction tool was reviewed by public health experts and not by someone from police department and experts in medicine dealing with trauma and injuries.
Missing data increase the risk of bias and may undermine the validity of research results38. However, the problem of missing data is ubiquitous and unavoidable in epidemiological research38. Even in developed countries, electronic health records were reported to have considerable missing data39. The problem of missing data is well recognized in health surveillance systems and has been dealt with by various methods40. In injury surveillance, imperfect data may still be a valuable source of information; work should therefore continue on improving the quality of these data10. The challenge of missing data can be addressed using multiple imputation or full information maximum likelihood methods30. Thus, though FIRs do not contain complete information on all the 12 MDS data items, these may still form the basis of an injury surveillance system, provided that any missing data are imputed. Information on the MDS data item 'nature of injury' which was captured only in 41.4 per cent cases, may also be supplemented from other documents such as hospital records or the police record-named charge sheet which has a medico-legal report attached with it. Efforts could also be made to improve capturing of data in FIRs by training of police personnel.
FIRs may not ascertain all injuries, and the percentage of injuries ascertained by police records may be less than that ascertained by hospital records, as has been found in the UK41. However, health records in India are either manual or are in disparate computer systems without interoperability or cross-sharing42. FIRs are presently a better source for obtaining countrywide information on injuries because of the availability of FIRs from all over India in a centralized, web-based system named Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS)43. The system is now operational in 94.8 per cent of police stations in India and, 5,176,457 FIRs were registered using the CCTNS34. Moreover, although not all injuries are reported to the police, the total number of injuries can be estimated from FIRs in 2019 using methods such as capture recapture44. This will make the problem of injuries more visible to policymakers and may trigger an appropriate policy response.
As per the Sections of the Indian Penal Code dealing with unintentional injuries, only acts of negligence causing injuries to other persons are considered a criminal offence and FIRs may be registered for such acts. Any self-sustained unintentional injuries (which are not required to be reported to the police) will therefore, be outside the scope of any such injury surveillance system. Moreover, access to police to register an FIR is affected by a person's socio-economic class and place of residence in an urban or a rural area. This can make FIRs less representative of all injuries and limit their use in an injury surveillance system.
In conclusion, information on injuries can be reliably extracted from FIRs using a data extraction tool designed in this study. Although FIRs do not always contain complete information on all the 12 data items in the MDS for injury surveillance, these may still usefully form the basis of an Indian injury surveillance system, provided that any missing data are imputed. We acknowledge the limitation that FIRs do not capture all unintentional injuries. However, in the absence of any other comprehensive data source, efforts can be made to improve the quality of data extraction and deal with missing data to make FIRs better suited for injury surveillance.
Acknowledgment:
Authors thank Delhi Police for granting permission and providing data for the study and acknowledge Drs Ankush Sanghai, Ranjit Ambad, Vishnu Udan, Chintan Parmar and Vaibhav from the Department of Health, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, for testing the data extraction tool and providing valuable feedback.
Financial support & sponsorship: This study was conducted as a part of the DrPH programme of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine of the first author (SSY), and his fee for the programme was partially paid by the Government of India.
Conflicts of Interest: None.
References
- Injuries and violence: The facts 2014. Geneva: WHO; 2014.
- Addressing the growing burden of trauma and injury in low- and middle-income countries. Am J Public Health. 2005;95:13-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Nations within a nation: Variations in epidemiological transition across the states of India, 1990-2016 in the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2017;390:2437-60.
- [Google Scholar]
- GBD compare viz hub. Available from: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbdcompare/
- Applicability of CDC guidelines toward the development of an injury surveillance system in the Caribbean. Inj Prev. 2001;7:245-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- 2012. Fatal Injury Surveillance in Mortuaries and Hospitals: A Manual for Practitioners. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/75351/9789241504072_eng.pdf
- Potential of using existing injury information for injury surveillance at the local level in developing countries: Experiences from Bangladesh. Public Health. 2000;114:133-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Development and use of a population based injury surveillance system: The all Wales Injury Surveillance System (AWISS) Inj Prev. 2002;8:83-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Developing injury surveillance in accident and emergency departments. Arch Dis Child. 1998;78:108-10.
- [Google Scholar]
- All wales injury surveillance system revised: Development of a population-based system to evaluate single-level and multilevel interventions. Inj Prev. 2016;22(Suppl 1):i50-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Public health surveillance: A tool for targeting and monitoring interventions. In: Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, eds. Disease control priorities in developing countries (2nd ed). New York: Oxford iversity Press; 2006. p. :997-1018.
- [Google Scholar]
- Under-reporting of road traffic injuries to the police: Results from two data sources in urban India. Inj Prev. 2008;14:360-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- 1973. The Code of Criminal Procedure. Available from: http://legislative.gov.in/sites/default/files/A1974-02.pdf
- Development and implementation of integrated road traffic injuries surveillance - India (IRIS-India): A protocol. Adv J Emerg Med. 2020;4:e35.
- [Google Scholar]
- Delhi Police Shanti Sewa Nyaya. Available from: http://www.delhipolice.nic.in/view-fir.html
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification Of Diseases and Related Health Problems. Geneva: WHO; 2004.
- International Classification of External Causes of Injury (ICECI). Avaiable from: https://www.who.int/classifications/icd/adaptations/iceci/en/
- Sample size requirements for training to a kappa agreement criterion on clinical dementia ratings. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2010;24:264-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Measurement in medicine: A practical guide. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2011.
- The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159-74.
- [Google Scholar]
- Injury Surveillance Guidelines. Geneva: WHO; 2001.
- Resolution concerning statistics of occupational injuries (resulting from occupational accidents. Geneva: ILO; 1998.
- EU-Injury Database: Operating Manual - version September 2016. Amsterdam: EuroSafe; 2016.
- NOMESCO Classification of External Causes of Injuries 2007
- Guidelines for the epidemiological surveillance on violence and injuries (Serie HCP/HCN, 01.01). Washington, DC: Pan American Health Organization; 2001.
- Status report - The Canadian Hospitals Injury Reporting and Prevention Program: a dynamic and innovative injury surveillance system. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2016;36:112-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Feasibility of establishing a UK wide injury database Avaiable from: https://www.rospa.com/rospaweb/docs/advice-services/home-safety/injury-causation-feasibilitystudy-final-report.pdf
- 2010. Available from: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/record/netherlandsinjurysurveillance-system-2010
- National Minimum Dataset for Injury Surveillance: NHMDS (Injury Surveillance). Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-health/national-minimum-dataset-forinjury-surveillance/contents/table-of-contents
- National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS). Available from: https://www.cpsc.gov/Research--Statistics/NEISS-Injury-Data
- Measures of interobserver agreement and reliability (2nd ed). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2010.
- San Francisco pedestrian injury surveillance: Mapping, under-reporting, and injury severity in police and hospital records. Accid Anal Prev. 2005;37:1102-13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Exploring data sources for road traffic injury in Cameroon: Collection and completeness of police records, newspaper reports, and a hospital trauma registry. Surgery. 2017;162:S24-31.
- [Google Scholar]
- Multiple imputation for missing data in epidemiological and clinical research: Potential and pitfalls. BMJ. 2009;338:b2393.
- [Google Scholar]
- Strategies for handling missing data in electronic health record derived data. EGEMS (Wash DC). 2013;1:1035.
- [Google Scholar]
- Potential adjustment methodology for missing data and reporting delay in the HIV Surveillance System, European Union/European Economic Area, 2015. Euro Surveill. 2018;23:1700359.
- [Google Scholar]
- Reporting of road traffic accidents in London: Matching police STATS19 data with hospital accident and emergency department data. Crowthorne: Transport Research Laboratory; 2002.
- 2018. Building Blocks. Available from: https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2019-11/NitiAayogBook_compressed_1.pdf
- 2020. National Crime Records Bureau. Available from: https://ncrb.gov.in/crime-and-criminal-tracking-network-systems-cctns
- Capture-recapture methods in epidemiology: Methods and limitations. Epidemiol Rev. 1995;17:243-64.
- [Google Scholar]






