Translate this page into:
Assessment of stress & related albuminuria in caregivers of severe mentally ill persons
Reprint requests: Dr Angshuman De, Anamika Flat No.6, P-68 South Park, PS + PO Bansdroni, Kolkata 700 070, India e-mail: angshude@yahoo.co.in
-
Received: ,
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
The family caregivers of patients with chronic diseases are known to undergo psychiatric stress leading to oxidative damage to glomerular membrane of kidney resulting in proteinuria. This study was aimed to compare current anxiety, depression levels and urinary albumin:creatinine ratio between primary caregivers of chronic mental patients and matched controls, and also whether the urinary albumin : creatinine ratio is correlated with stress factors (state and trait anxiety level, depression and caregiver burden) amongst caregivers.
Methods:
The present cross-sectional study included 131 subjects (93 primary caregivers of patients with major mental illness as cases and 38 normal controls). They completed the Burden Assessment Schedule of SCARF, State Trait Anxiety Inventory and Beck's Depression Inventory. A spot urine sample was tested for urinary albumin : creatinine ratio from all study subjects.
Results:
Mean values of current State and Trait anxiety, depression, urinary albumin:creatinine ratio were significantly higher in caregivers than controls (P < 0.001). Urinary albumin : creatinine ratio was significantly correlated (P < 0.001) with State and Trait anxiety level, depression as well as caregiver burden.
Interpretation & conclusions:
The study demonstrated depression, anxiety and albuminuria amongst primary caregivers of patients with mental illness. Increase in the caregivers’ burden, depression and anxiety resulted in an increase in the urinary albumin: creatinine ratio. This indicates that psychological stress is one of the determinants of albumin excretion rate in otherwise healthy subjects.
Keywords
Albuminuria
albumin : creatinine ratio
anxiety
depression
primary caregivers
schizophrenia
It has been reported that over 60 per cent of patients with major mental illness are supposed to live with at least one primary caregiver, the main provider of physical and emotional support for them1. The demands of caring for a chronic234 and mentally ill relative have an emotional, social and practical stress on the caregivers5678 leading to increase in glomerular membrane permeability of kidney910 and subsequently resulting in an increase in urinary albumin excretion. Several studies11121314 have been carried out to evaluate the relationship between stress and urinary albumin excretion. The present study was undertaken to compare the current anxiety and depression level, urinary albumin:creatinine ratio in the primary caregivers of patients with major mental illness with healthy controls, and to observe the relationship, if any, between stress factors (state and trait anxiety level, depression, caregiver burden) and urinary albumin:creatinine ratio among caregivers of patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
Material & Methods
The present hospital based, cross-sectional study was undertaken between May to June 2010 in the Department of Psychiatry, Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, India. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Primary caregivers of patients with major mental illness, attending the psychiatry department of Medical College, Kolkata, were selected by random sampling method. Along with the general health assessment, routine urine, haematological and biochemical examinations were done for both cases and controls to rule out diseases mentioned in exclusion criteria.
The primary caregiver was identified as an adult relative (age 16-60 yr man/woman) living with a patient, in the same environment for minimum six months, and felt most responsible for the patient. All subjects suffering from any inherited or acquired diseases leading to albuminuria like glomerulonephritis, glomerular disease of diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, amyloidosis, hypertension, infectious diseases like HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, malaria, severe mental illness or dementia, history of drug intake liable to cause albuminuria were excluded from the study.
Among the primary caregivers, 93 (45.56 ± 9.56 yr, 33 women) were selected as cases. Only thirty eight controls (46.81 ± 9.27 yr including 13 women) could be selected from apparently healthy age, sex, socio-economic status matched individuals (hospital staff, attendants of other patients) who did not have to bear a chronic caregiver burden and did not have other diseases or conditions, mentioned in exclusion criteria. The cases and controls were informed about the purpose of the study and written informed consent for inclusion in the study was obtained.
Primary caregivers were requested to give their response to the ‘Primary Caregiver (PC) questionnaire’. It was a structured questionnaire proforma containing socio-demographic and care-giving details. After that, caregivers completed the Caregiver Burden Assessment Schedule (BAS) of SCARF (Schizophrenia Research Foundation)1516, validated Bengali version of State Trait Anxiety Inventory Form Y (STAI)1718 and validated Bengali version of Beck's Depression Inventory (BDI)1920. A midstream and clean-catch spot urine sample was tested mainly in the morning (during Psychiatric Outdoor hours: 0900 - 1400 h) for urinary albumin:creatinine ratio21 using ERBAIM Mannheim kits (Germany, India) for quantitative determination of urinary microalbumin and creatinine (Jaffe's method22. The same procedure was repeated for the control sample.
Statistical analysis: The data were analyzed using SPSS software version 14 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). Statistically significant difference was determined by the Student's t test. Correlation cofficient was calculated according to the Brave-Pearson function. Regression analysis and Fisher exact test were used as statistical tool.
Results
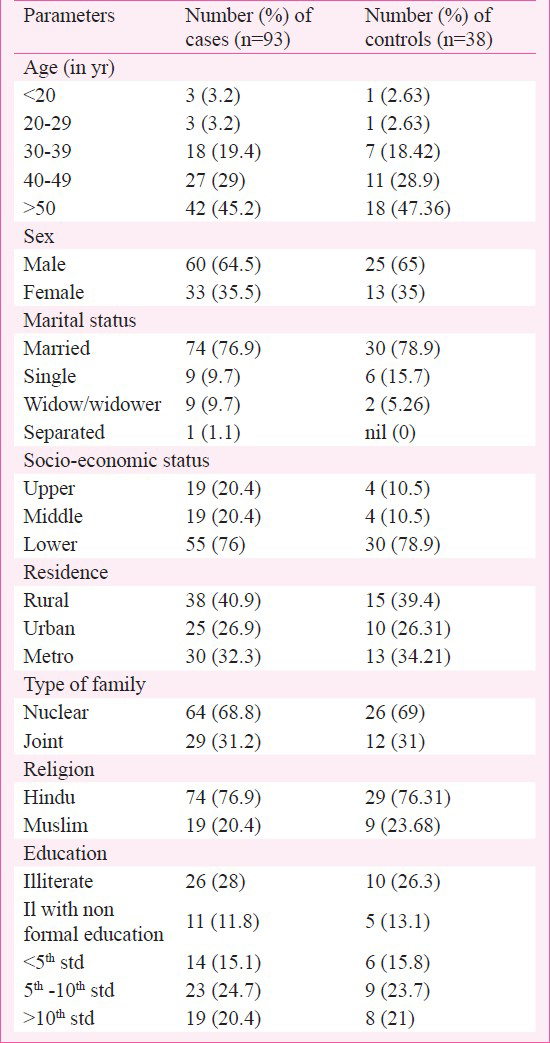
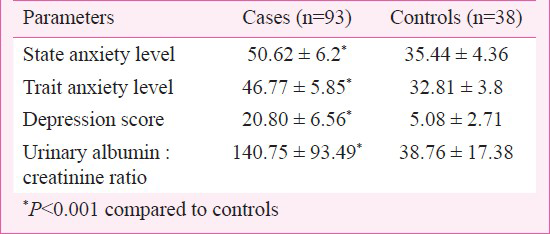
The socio-demographic pattern of caregivers and controls is shown in Table I. The State anxiety level, Trait anxiety level, depression score and caregivers’ burden were significantly higher in caregivers as compared to controls (P < 0.001) (Table II). Urinary albumin-creatinine ratio was also significantly higher in cases than in controls (P < 0.001). Of the 93 caregivers, 88 (94.6%) had microalbuminuria (30-300 mg/g of creatinine) and five (5.4%) had macroalbuminuria (>300 mg/g of creatinine). None of the caregivers was in the normal range (0-30 mg/g of creatinine) of urinary albumin-creatinine ratio, however, 10 of 38 controls (26.3%) were normal.
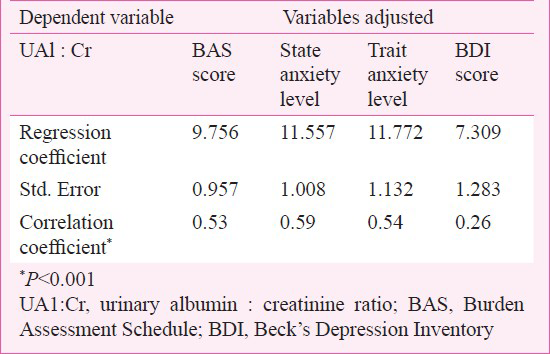
Multiple regression analysis in caregivers showed that urinary albumin-creatinine ratio demonstrated a significant positive correlation with caregiver burden, current anxiety level and depression score (P < 0.001) (Table III).
Discussion
This study showed that there was a raised level of depression, State and Trait anxiety level as well as caregivers burden in cases compared to control. Several other studies have reported similar findings232425. The urinary albumin:creatinine ratio (UAl:Cr) was found to be significantly higher among the cases than controls as shown in earlier studies11121314. In our study, none of the controls had macroalbuminuria. Though 73.7 per cent controls had microalbuminuria, but highest value was 56.14 mg/g which was on the lower side of microalbuminuria range (30-300 mg/g of creatinine) whereas 94.6 per cent of cases showed high microalbuminuria with highest value being 293 mg/g of creatinine. All biochemical reference values are known to vary depending on the type of population, race, ehnicity, which may be a reason for higher limit of urinary microalbumin in control population26272829.
Multiple regression analysis in caregivers demonstrated a significant positive correlation between UAl:Cr ratio and caregiver burden, current anxiety level and depression. It was evident from the results that if there was an increase in the stress factors, there was obvious increase in the urinary albumin:creatinine ratio. This result can be explained by the fact that increased burden, depression and anxiety lead to increased physical oxidative stress that affects the renal system causing increased albuminuria. Ratnakar et al9 have also shown that stress leads to increased glomerular permeability to proteins. As during screening, no causes of raised value of Alb:Cr ratio was noted, this difference between cases and controls could be ascribed to mental and social stress of caregivers. Though caregivers appear normal, but ongoing mental stress due to caregiving may generate physical stress of which albuminuria may be one early sign.
The limitations of the study was its small sample size; the number of controls was not equal to the cases. Being a short study, it was not possible to collect urine for three times on different days. So the physiological variations [high intra-individual CV (30-50%) and diurnal variation (50-100% higher during the day)]29 could influence the albumin excretion in urine which should be kept in mind while planning for larger population study which may establish urinary albumin: creatinine ratio as a simple non-invasive screening test for primary caregiver burden assessment.
Acknowledgment
The first author (AD) acknowledges the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, for providing Short Term Studentship.
References
- Deliverability of psychoeducational family management. Schizophr Bull. 1994;20:547-56.
- [Google Scholar]
- Anxiety, depression, and quality of life in caregivers of patients with cancer in late palliative phase. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1185-91.
- [Google Scholar]
- Measures of psychological stress and physical health in family caregivers of stroke survivors: a literature review. J Neurosci Nurs. 2010;42:128-38.
- [Google Scholar]
- The impact of stroke on the well-being of the patient's spouse: an exploratory study. J Clin Nurs. 2007;16:264-71.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparison of the extent and pattern of family burden in affective disorders and schizophrenia. Indian J Psychiatry. 1995;37:105-12.
- [Google Scholar]
- Depression among primary caregivers of Schizophrenic patients. Ann Pak Inst Med Sci. 2005;1:101-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Predictors of burden and infectious illness in schizophrenia caregivers. Psychosom Med. 1999;61:411-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Family caregiving in schizophrenia: domains and distress. Schizophr Bull. 1998;24:609-18.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of anxiety, depression and urinary protein excretion among the family caregivers of advanced cancer patients. Biol Psychol. 2008;79:234-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Renal adaptation to stress: a possible role of endothelin release and prostaglandin modulation in the human subject. J Lab Clin Med. 1997;129:462-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Transient proteinuria in emergency medical admissions. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:1031-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnostic and prognostic significance of proteinuria selectivity index in glomerular diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;297:73-83.
- [Google Scholar]
- The Burden Assessment Schedule (BAS). WHO Regional Publications, South-East Asia, Series No. 27. New Delhi: World Health Organization, Regional Office for South-East Asia; 1998. p. :15-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Assessment of subjective well-being: The subjective well-being inventory (SUBI). Regional Health Paper, SEARO, No. 24. New Delhi: World Health Organization, Regional Office for South-East Asia; 1992.
- [Google Scholar]
- Manual for state-trait anxiety inventory (self-evaluation questionnaire) Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press; 1970.
- [Google Scholar]
- Manual for the Beck depression inventory-II. San Antonio, Tex: Psychological Corporation; 1996.
- [Google Scholar]
- Adoption of beck depression inventry into Bengali and its clinical validity. Bull Indian Psychiatr Soc. 1995;5:5-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Quantitation of proteinuria by the use of protein-to-creatinine ratios in single urine samples. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:943-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Analytical reviews in clinical biochemistry. The estimation of creatinine. Ann Clin Biochem. 1986;23:1-25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Perceived stigma and depression among caregivers of patients with bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 2007;190:535-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- A systematic review of the prevalence and covariates of anxiety in caregivers of people with dementia. Int Psychogeriatr. 2007;19:175-95.
- [Google Scholar]
- Emotional distress and quality of life in caregivers of patients awaiting lung transplant. J Psychosom Res. 2005;59:1-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Smoking is related to albuminuria and abnormal renal function in nondiabetic persons. Ann Intern Med. 2000;133:585-91.
- [Google Scholar]
- High normal levels of albuminuria and risk of hypertension in Indo-Asian population. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(Suppl 3):58-64.
- [Google Scholar]
- Muscular mass and overestimation of microalbuminuria by urinary albumin/creatinine ratio. Hypertension. 2006;47:56-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kidney Function Tests. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE, eds. TIETZ textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnotis (4th ed). New Delhi: Elsevier Publication; 2005. p. :797-835.
- [Google Scholar]






