Translate this page into:
Antimicrobial resistance in Shigella - rapid increase & widening of spectrum in Andaman Islands, India
Reprint requests: Dr Subarna Roy, Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), Post Bag No.13, Port Blair 744101, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, India e-mail: roys@icmr.org.in pblicmr@sancharnet.in
-
Received: ,
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background & objectives:
Shigellosis is known to be a major cause of acute childhood diarrhoea in Andaman & Nicobar Islands, India. Rapid emergence of antibiotic resistance warrants continuous monitoring of sensitivity pattern of bacterial isolates. We report here the salient findings of an ongoing study on shigellosis in Andaman Islands, India, with regards to change in drug resistance pattern during the past one decade.
Method:
During 2006-2009, stools samples from 412 paediatric diarrhoea patients were collected and processed for isolation and identification of Shigella spp. Susceptibility to 22 antimicrobial drugs was tested and MICs were determined for 3rd generation cephalosporins, quinolones, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid combination and gentamicin. Drug susceptibility pattern of these isolates were compared with that of 33 isolates obtained during 2000-2002.
Results:
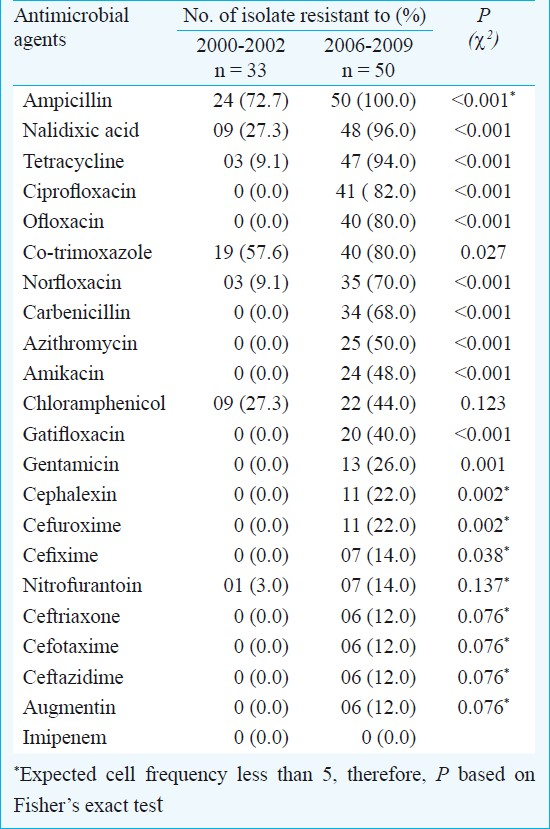
Shigella isolates were recovered from 50 of 412 stool samples processed. Resistance to ampicillin, nalidixic acid, tetracycline and ciprofloxacin was observed in 100, 96, 94 and 82 per cent of the isolates, respectively. The frequency of resistance to these drugs was significantly (P<0.001) higher than that observed during 2000-2002. Resistance to seven drugs was observed in 2000-2002, whereas resistance to 21 drugs was seen during 2006-2009. The number of drug resistance pattern increased from 13 in 2000-2002 to 43 in 2006-2009. Resistance to newer generation fluoroquinolones, 3rd generation cephalosporins and augmentin, which was not observed during 2000-2002, appeared during 2006-2009.
Interpretation & conclusions:
The frequency of resistance among Shigella isolates has increased substantially between 2000-2002 and 2006-2009 and the spectrum of resistance has widened. At present, the option for antimicrobial therapy in shigellosis in Andaman is limited to a small number of drugs. Continuous local monitoring of resistance patterns is necessary for the appropriate selection of empirical antimicrobial therapy.
Keywords
Antibiotic
diarrhoea
frequency
paediatric
resistance
Shigella
widening spectrum
Shigella is a major cause of dysentery throughout the world and is responsible for 5-10 per cent of diarrhoeal illness in many areas1. It has been estimated that 91 million individuals worldwide contract shigellosis each year and among them 1.1 million die2. About, 4, 10000 (40%) of these deaths occur among Asian children3. Antibiotic therapy reduces the duration of Shigella dysenteriae infection and, therefore, is recommended, for the treatment of moderate to severe dysentery4. Appropriate antibiotic treatment of shigellosis depends on identifying resistance patterns5. Rapid emergence of resistance warrants the need for continuous monitoring of sensitivity patterns67 and the choice of antibiotic should be governed by periodically updated local antibiotic sensitivity patterns of Shigella isolates4.
Hospital based bacteriological surveillance has identified shigellosis as endemic and a major cause of acute childhood diarrhoea in Andaman and Nicobar Islands89. As in the case of most other developing countries, S. flexneri 2a was the commonest isolate. However, species and serotypes composition of Shigella isolates showed considerable variation over the years810 and so did their drug resistance patterns. A study on microbiological, clinical and epidemiological aspects of childhood diarrhoea among the population of Andaman and Nicobar Islands was initiated by Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), Port Blair in these Islands a few years back. The objectives of the study were to estimate the proportional morbidity ratio of childhood diarrhoea due to infection with different enteric pathogen, assess the emergence of drug resistance among bacterial enteric pathogens, describe the epidemiology of childhood diarrhoea in the islands and to assess the distribution of toxigenic genes among enteric pathogens and the their association with clinical presentation, severity and outcome of disease. In this report, we describe the drug resistance pattern of the isolates of Shigellae obtained as part of the study and a comparison with those obtained earlier.
Material & Methods
Patients and specimens: Diarrhoea patients in the age group of 6 months - 14 yr admitted to the wards of G.B. Pant Hospital and Primary/Community Health Centers present throughout the Andaman & Nirobar Islands from January 2006 to December 2009, were included in the study. Attempt was made to include all available in-patients in the above age group with diarrhoea without adopting any sampling procedure. Stool samples were collected in stool vials (Hi-Media, Mumbai) prior to the administration of antimicrobials. The samples were immediately brought to the Regional Medical Research Centre (RMRC), Port Blair, laboratory maintaining 4°C for processing. Written consent was taken from the patient/guardian prior to collection of samples. The study was performed at RMRC, Port Blair and the study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Centre.
Microbiological examination: The stools samples were processed and the Shigella isolates were identified and confirmed following standard techniques11. The primary culture medium for Shigella isolation was deoxycholate citrate agar (DCA) (Hi-Media, Mumbai, India) and Hektoen Enteric Agar (HEA) (Hi-Media, Mumbai, India). The isolation of Shigella was followed by biochemical characterization and serotyping using group specific antisera (Denka Seiken, Japan). Antibiotic susceptibility testing was carried out using the disc diffusion method, according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines11 using antibiotic discs (Hi-Media, India) which included ampicillin (AMP, 10 μg), tetracycline (TET, 30 μg), co-trimoxazole (CoT, 20 μg), nalidixic acid (NAL, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 30 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), norfloxacin (NOR, 10 μg), nitrofurantoin (NIT, 300 μg), ofloxacin (OFX, 5 μg), gatifloxacin (GAT, 5 μg), amikacin (AMK, 30 μg), azithromycin (AZM, 30 μg), imipenem (IMP, 30 μg), chloramphenicol (CHL, 30 μg), carbenicillin (CAR, 100 μg), cefixime (CFM, 30 μg), cefuroxime (CXM, 5 μg), cephalothin (CEF, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), cefotaxime (CTX, 30 μg), ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg) and augmentin/amoxicillin-clavulanic acid combination (AMC, 30 μg). Control strains Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 were included in each test. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, ceftazidime and cefotaxime), quinolones (nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and gatifloxacin), augmentin and gentamicin were determined by E-test (AB Biodisk, Sweden). Extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) production was detected using the double-disk synergy method with ceftazidime-clavulanic acid (CAC, 30/10 μg) and ceftriaxone-clavulanic acid (CAC, 30/10 μg).
Some of the drugs such as nitrofurantoin and aminoglycosides were included though these are not recommended for treatment of shigellosis, resistance to these could be used as a phenotypic characteristic to study the evolution of the pathogen over a period of time.
Statistical analysis: The proportions of isolated Shigella isolates resistant to each of the antibacterial drugs for 2006-2009 were calculated, and compared with those of 2000-2002, and statistical significance was tested by χ2 test, or Fisher's exact test when the expected number in any cell was less than five.
Results
Species distribution: Of the 412 stool samples processed, 50 (12.1%) yielded Shigella isolates. Among these, 34 (68%) were S. flexneri, 10 (20%) S. sonnei and 6 (12%) were S. dysenteriae. No S. boydii was isolated during the study period. In 2006, 2007 and 2008 S. flexneri was the dominant strain isolated whereas in 2009 almost equal numbers of S. flexneri (7) and S. sonnei (8) were isolated.
Antimicrobial resistance: All the 50 Shigella isolates obtained during the study period were resistant to ampicillin, 96 per cent to nalidixic acid (MIC, 0.5 to >256 μg/l), 94 per cent to tetracycline, 82 per cent to ciprofloxacin (MIC, 1 to >256 μg/l), 80 per cent to ofloxacin (MIC, 1 to >256 μg/l) and 70 per cent to norfloxacin (MIC, 0.5 to >256 μg/l) (Table I). About 40 per cent of the isolates were also resistant to fourth generation fluoroquinolone viz., gatifloxacin (MIC, 2 to 8 μg/l). A significant proportion of the isolates were resistant to the two aminoglycosides used in the study viz. amikacin (48%) and gentamicin (26%, MIC 0.5 to >256 μg/l). Resistance to third generation cephalosporins also appeared to be emerging as 12 per cent showed resistance to the three third generation cephalosporins used viz. ceftriaxone (MIC, 30 to >256 μg/l), cefotaxime (MIC 5 to >256 μg/l) and ceftazidime (MIC 5 to >256 μg/l). Some isolates were also resistant to augmentin (12%, MIC 5 to >256 μg/l). All the isolates were sensitive to imipenem. Resistance to fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides was more common among S. dysenteriae as compared to S. flexneri, but the number of S. dysenteriae isolates was small for these differences to be statistically significant. Only five isolates were confirmed to produce ESBL due to an increase of 5 mm in zone diameter around ceftazidime-clavulanic acid and ceftriaxone -clavulanic acid disc compared to the zone around the ceftazidime and ceftriaxone disc respectively12.
The 50 isolates obtained during the study period (2006-2009) showed 43 drug resistance patterns, all of which involved three or more drugs. Among these drug resistance patterns, one (2.3%) was resistance to three drugs, seven (16.3%) to 4-5 drugs, nine (20.9%) to 6-7 drugs and 13 (30.2%) each to 8-9 drugs and 10 or more drugs. Forty nine (98%) out of the 50 isolates were resistant to four or more drugs.
Thirty three isolates obtained during the period 2000-2002 were retested for the new drugs which were not used at that time. Resistance to 7 of the 22 antibacterial drugs was observed in one or more of the 33 isolates obtained in 2000-2002 whereas resistance to 21 of the 22 drugs was observed during the present period. In 2000-2002, ampicillin and co-trimoxazole were the only two drugs against which more than 50 per cent of the isolates showed resistance while in 2006-2009 there were nine drugs, including norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, carbenicillin and azithromycin, to which more than 50 per cent of the isolates were resistant. The proportions of resistant isolates showed an increase from 2000-2002 to 2006-2009 in the case of 21 of the 22 antibiotics tested, the only exception being imipenem, resistance to which was observed neither in 2000-2002 nor in 2006-2009. This increase in the proportions of resistant isolates between the two study periods was significant (P<0.05) in the case of 15 of the 21 drugs against which resistance was observed. The most noticeable increase in the resistance was against nalidixic acid (27.2 to 96%), ampicillin (72.7 to 100%) and co-trimoxazole (57.6 to 80%). During the present study period, more than 90 per cent isolates were resistant to nalidixic acid, ampicillin, tetracycline and 80-90 per cent of these to the other commonly used drugs such as ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and co-trimoxazole13.
In 2002, the number of drug resistance patterns observed was only 13 whereas during the present study 43 patterns were observed indicating a widening of the spectrum of drug resistance pattern during the intervening period. In 2002, only 21 per cent of the isolates were resistant to more than three drugs and none was resistant to more than five drugs whereas during 2006-2009, 41 of the 50 isolates (82%) were resistant to more than five drugs. The median number of drugs the isolates were resistant was 2 in 2002 and 9 during 2006-2009 (Fig.).
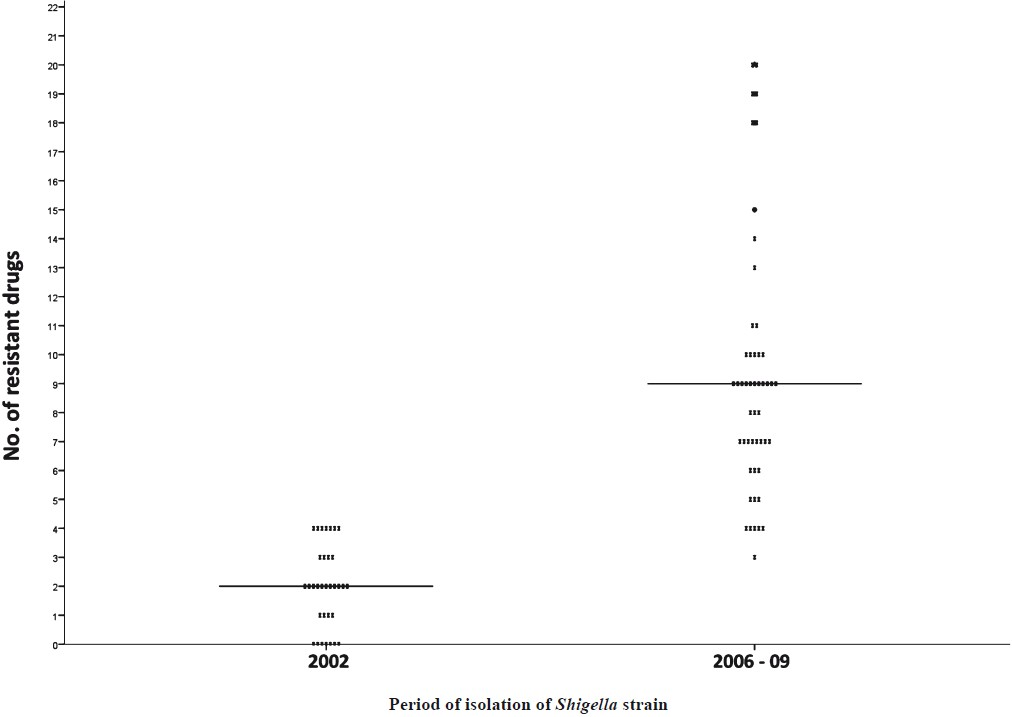
- Distribution of Shigella isolates in 2002 and 2006-2009 by number of antimicrobial the isolate was resistant to.
Discussion
Changing patterns of antimicrobial susceptibilities among Shigella isolates pose major difficulties in selecting an appropriate drug for the treatment of shigellosis1415. The present study demonstrated the increasing spectrum of antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates during the past one decade in these islands. There has been a decline in cases of acute childhood diarrhoea during the two years that followed the Great Asian Tsunami of December 200416. However, during 2008-2009 there was an upsurge in the number of cases and the antimicrobial resistance spectra of Shigella isolates were much wider than those observed earlier.
Resistance to antimicrobial agents used to treat shigellosis in young children, namely ampicillin, was observed in 1990s in the islands89. This has been increasing over the years and at present all the isolated Shigellae are resistant to this drug. Presence of resistance to tetracycline showed a ten-fold increase from 9 to 94 per cent during this decade. Nalidixic acid became the mainstay of antibacterial therapy in shigellosis. Resistance to this drug was first reported in these islands in late 90s13 and by 2006-2009 almost all the isolates became resistant to it. Other quinolones such as norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin then became the primary choice for antibacterial therapy. Although fluoroquinolones are recommended as the drugs of choice for shigellosis by World Health Organization14, emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance among Shigella spp. has now been documented in many countries17–19. At present, alternate drugs such as the third generation cephalosporins are being used commonly. The present study shows that Shigella strains are rapidly acquiring resistance to these drugs as well. The emergence of plasmid borne resistance to these cephalosporins further reduces the choice of drugs for the treatment of shigellosis. The genetic transfer of drug resistance genes may not be of immediate concern for the treating clinicians, but will pose a potential problem in the future. ESBLs have evolved greatly over the last 20 yr. Their presence, plus the potential for plasmid-mediated quinolone and carbapanem resistance, will be sure to create significant therapeutic problems in the future.
A larger proportion of S. dysenteriae, which is usually the cause of outbreaks and severe disease, is resistant to multiple drugs as compared to other Shigella spp. In case of any future outbreak of S. dysenteriae in the islands the clinicians would be left with little choice of antimicrobial drugs to treat patients.
Widespread selective pressure and efficient dissemination channels for multi-drug resistant organisms are major factors that might have contributed to the rapid emergence and spread of resistant organisms20.
In conclusion, the emergence of resistance to several new drugs such as flouroquinolones, 3rd generation cephalosoprins, and macroilides in Shigellae is a cause of great concern not only at local level but at regional level also. A comprehensive strategy for resistance control involving regulation of drug availability, antimicrobial drug quality assurance, adequate surveillance and discouraging the culture of antimicrobial abuse needs to be evolved21. A network of laboratories for real-time monitoring of antibiotic resistance among enteric pathogens and timely dissemination of such information to the clinicians for modification of treatment strategy is the need of the hour.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr S.C. Sehgal, former Director, RMRC, Port Blair, for initiation of diarrhoeal surveillance in the islands. The authors acknowledge the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, for providing financial grant and Dr P. Vijayachari, Director, RMRC, for administrative support.
References
- Genetic characterization of multidrug resistance in Shigella spp. from Japan. J Med Microbiol. 2006;55:1685-91.
- [Google Scholar]
- Global burden of Shigella infections: implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull World Health Organ. 1999;77:651-66.
- [Google Scholar]
- Shigellosis: disease burden, epidemiology and case management. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2005;80:94-9. [No authors listed]
- [Google Scholar]
- Antibiotic therapy for Shigella dysentery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD006784.
- [Google Scholar]
- Growing antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51:427-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rethinking options for the treatment of shigellosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992;30:243-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Frequency of isolation of various subtypes and antimicrobial resistance of Shigella from urban slums of Karachi, Pakistan. Int J Infec Dis. 2009;13:668-72.
- [Google Scholar]
- Existing status of shigellosis in Andaman & Nicobar Islands. Indian J Med Res. 1996;103:134-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Shigella infections among children in Andaman - an archipelago of tropical islands in Bay of Bengal. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:43-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Distribution of Shigella enterotoxin genes and secreted autotransporter toxin gene among diverse species and serotypes of Shigella isolated from Andaman Islands, India. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11:1694-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) In: Performance standards for antimicrobial disc susceptibility tests. Approved standard M2-A10. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI; 2007.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rapid emergence of third- generation cephalosporin resistance in Shigella sp.isolated in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Microb Drug Resist. 2011;17:329-32.
- [Google Scholar]
- Emergence of Nalidixic acid-resistant Shigella sonnei in acute-diarrhoea patients on Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:1483.
- [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. 2005. Guidelines for the Control of Shigellosis, including epidemics due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1. Geneva: WHO; Available from: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2005/9241592330.pdf
- [Google Scholar]
- Changing patterns of serotypes and antimicrobial susceptibilities of Shigella species isolated from children in Calcutta, India. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2001;54:121-2.
- [Google Scholar]
- Acute diarrhea in children after 2004 tsunami, Andaman Islands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:849-50.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fluoroquinolone-resistant Shigella dysenteriae type 1 in northeastern Bangladesh. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4:607-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial susceptibility of Shigella sonnei isolates in Japan and molecular analysis of S.sonnei isolates with reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:1203-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance in Shigella isolated from Andaman & Nicobar Islands, India. Indian J Med Res. 2010;131:720-2.
- [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries. Part I: recent trends and current status. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:481-93.
- [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries. Part II: strategies for containment. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:568-80.
- [Google Scholar]






