Translate this page into:
An unusual case of angiomatous polyp
*For correspondence: drhetalent@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A 57 yr old male† presented to the department of ENT at King Edward Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India, in May 2019, with a right cheek swelling, nasal obstruction, epistaxis and paraesthesia (Fig. 1). Endoscopy revealed a fleshy nasal mass (Fig. 2). Imaging was suggestive of an encapsulated heterogeneous lesion within the maxilla with erosion of the sinus walls (Fig. 3). Biopsy was suggestive of a haemangioma. Complete excision via lateral rhinotomy incision (Fig. 4) was performed, and the final diagnosis of angiomatous polyp was made by histopathological confirmation (Fig. 5). The patient was followed up after one month with a well-healed facial scar (Fig. 6).
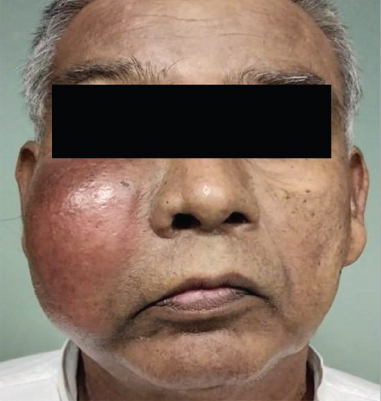
- Patient with swelling on the right cheek.
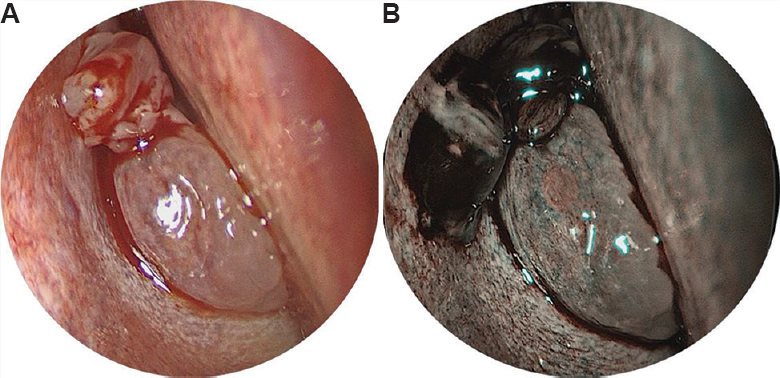
- (A) Diagnostic nasal endoscopy revealed a pink fleshy mass which bled to touch, completely filling the right nasal cavity. (B) Narrow band imaging of the nasal mass shows Ni classification type 2 vascular pattern with enlarged, oblique and arborescent vessels and fine white lines of interepithelial papillary capillary loops, which is suggestive of benign lesion.
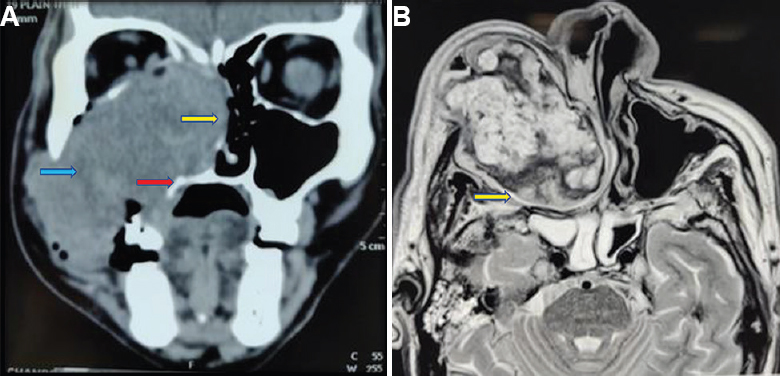
- (A) Contrast computed tomography of paranasal sinus, coronal cuts showing an expanding heterogeneous mass with its epicentre in the maxillary sinus. Yellow arrow shows destruction of the nasal septum with extension to the opposite side. Red arrow shows the erosion of the palate. Blue arrow shows the erosion of the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus. (B) Axial section of T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging also showed the well-encapsulated heterogeneous mass, yellow arrow shows the capsule.
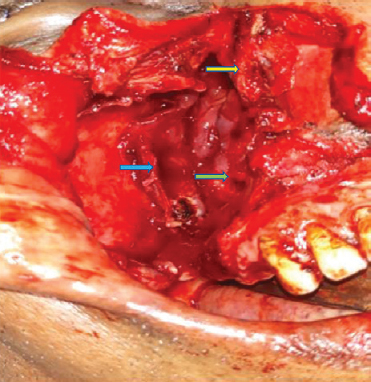
- Post-excision cavity with yellow arrow shows superior turbinate. Green arrow shows the nasopharynx. Blue arrow shows the wall of pterygopalatine fossa.
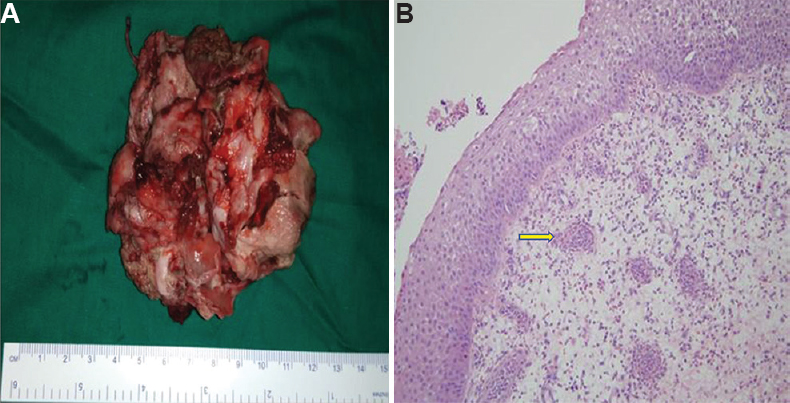
- (A) Excised mass in piece meal. (B) Histopathological examination showing respiratory epithelium lining with multiple, thin-walled dilated vessels in a pool of eosinophilic granulomas suggestive of angiomatous polyp, which is represented by yellow arrow.
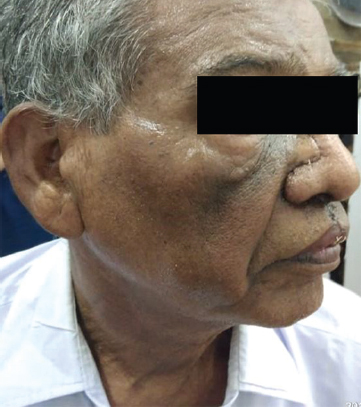
- Outcome after one month of surgery with a healed scar.
Angiomatous polyps are rare variants of sino-nasal polyps which mimic malignancy. Surgical excision yields a positive outcome with less morbidity.
Conflicts of Interest: None.





