Translate this page into:
Multiple periarticular nodules diagnosed as gout on fine-needle aspiration cytology
* For correspondence: anjali@knee.in
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A 45 year old male† known case of diabetes mellitus and hypertension presented with multiple painless nodules over both hands (at right wrist and multiple interphalangeal joint), both foot and left knee since four years at the surgical outpatient department (OPD) at Vadilal Sarabhai General Hospital, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India, in February 2016. On examination, nodules were not tender, non-mobile and erythematous (Fig. 1). Radiograph of hands (Fig. 2), foot and left knee showed subcutaneous nodule. The differential diagnosis included metastasis, primary tumour and gout since the previous history did not reveal any episodic bouts of arthritis.
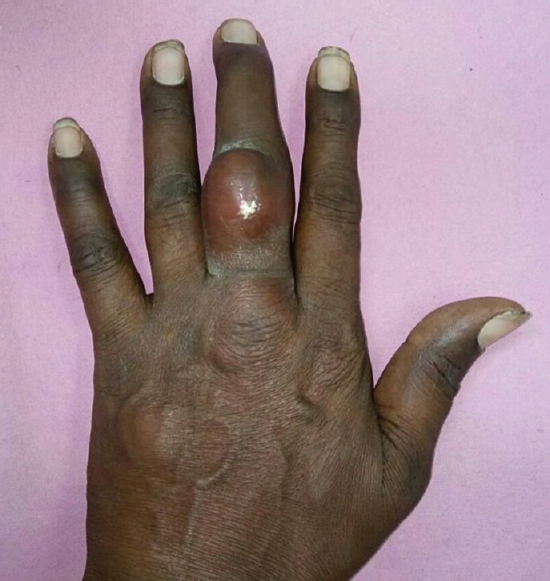
- Left hand of patient showing a non-mobile and erythematous nodules on the dorsal aspect of the middle phalanx of the middle finger.

- Radiographs of the both hands showing the absence of any bony involvement. A soft-tissue shadow of the subcutaneous nodule over middle phalanx of the left middle finger is seen.
Fine-needle aspiration from multiple swelling was performed using a 22 mm gauge needle. Aspirate yielded chalky white amorphous material. The aspirated material was fixed with methanol and stained by haematoxylin and eosin. Light microscopy of the slides showed eosinophilic slender needle-shaped crystals with pointed ends distributed singly or in groups (Fig. 3). These showed strong birefringence under polarized light consistent with monosodium urate crystals (Fig. 4).
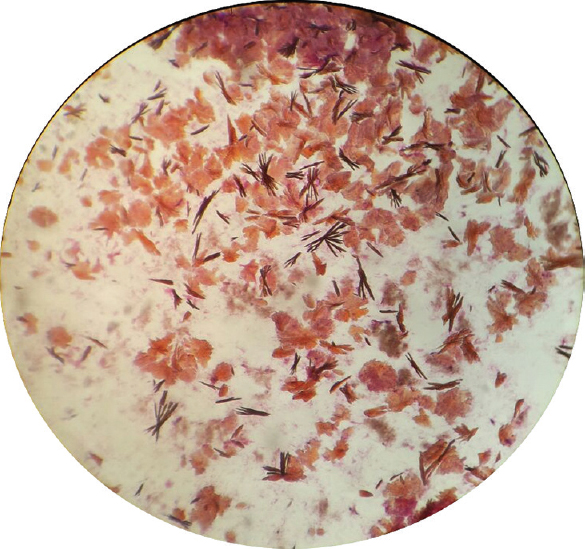
- Light microscopy (×40) of the fluid aspirated from the subcutaneous nodule of the left middle finger, showing eosinophilic slender needle-shaped crystals with pointed ends distributed singly and in groups.
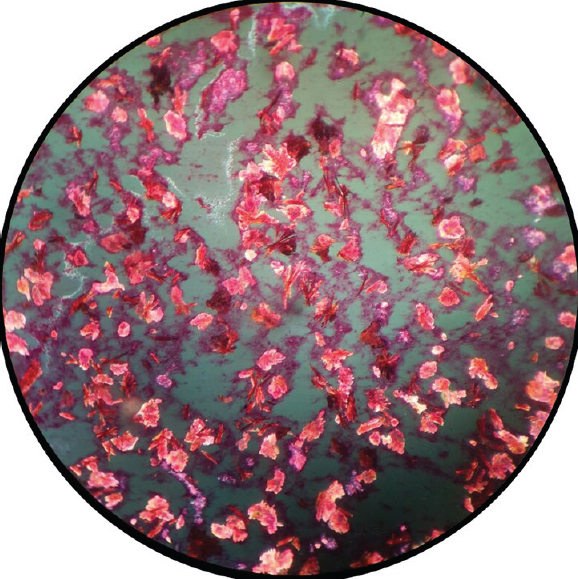
- Polarized microscopy of the fluid aspirated from the subcutaneous nodule of the left middle finger, showing strong birefringence of the crystals.
On further examination, the patient's serum uric acid was 10.59 mg/dl (normal 3.5-7.2 mg/dl), and the diagnosis of gout was confirmed. The patient was treated with oral analgesics and allopurinol 200 mg and was completely symptom free at follow up (approximately eight months after commencing treatment).
Acknowledgment
Authors acknowledge the contribution of Dr Bhavesh Dave, Head of the Surgical Unit, for providing the clinical details and pictures.
Conflicts of Interest: None.





