Translate this page into:
Approaches used to improve epigenetic reprogramming in buffalo cloned embryos
For correspondence: Dr Naresh L. Selokar, Division of Animal Physiology & Reproduction, ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes, Hisar 125 001, Haryana, India e-mail: selokarnareshlalaji@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
The reproductive cloning in buffalo in India has been started using a simplified somatic cell nuclear transfer technique named handmade cloning. Since the birth of first cloned female buffalo in 2009, a number of buffalo clones have been produced in India by utilizing different types of donor cells such as ear cells, embryonic stem cells, semen somatic cells and urine somatic cells. The use of buffalo cloning on a large scale is restricted due to low pregnancy rates and poor calf survival. Considerable attempts have been made to improve the overall buffalo cloning efficiency, particularly by modifying epigenetic reprogramming of cloned embryos. Previous studies have demonstrated that chemical epigenetic modifiers such as trichostatin A and 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine, m-carboxycinnamic acid bishydroxamide can be used to treat donor somatic cells and reconstructed fused embryos to correct the epigenetic reprogramming to enhance the overall cloning efficiency in terms of live birth rates.
Keywords
Birth rate
buffalo
cloned
embryos
epigenetics
reprogramming
Introduction
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is one of the most successful tools of assisted reproductive techniques, which has been used to produce identical copies of elite domestic animals such as cattle, buffalo and sheep, goats and pigs1, and for drug production (biopharming), regenerative medicine (nuclear stem cell lines to cure diseases) and conservation of genetic resources (cloning of endangered species)2. Buffalo SCNT has enormous potential applications; however, the technique has been suffering from low live offspring birth rate (<2%) after transfer of cloned blastocysts34. Many abnormalities such as high rate of early abortion, large offspring syndrome, placental defects and health issues of born clones have been reported in cloned animals35. These developmental abnormalities are conceivably accountable for poor cloning efficiency and it is believed that abnormal epigenetic reprogramming of differentiated somatic cells is the main cause of poor cloning efficiency across the species, including buffalo.
Incorrect or faulty epigenetic reprogramming of donor cells by recipient oocytes during SCNT is one of the key factors responsible for the low cloning efficiency; therefore, for achieving correct nuclear reprogramming, the epigenetic status of donor cells or cloned embryos needs to be manipulated in such a way that generated cloned blastocysts would be more closely similar to in vivo or in vitro fertilized (IVF) embryos. To correct the nuclear reprogramming and to improve the developmental competence of cloned embryos, various approaches have been employed either in somatic cells or in cloned embryos; however, significant success in the term of live birth rate has not been achieved. Here we discussed about in vitro studies in which epigenetic modifiers were used to correct reprogramming of SCNT buffalo embryos.
Methods of buffalo cloning
The buffalo can be cloned using two broadly used SCNT techniques, first is a classical SCNT in which micromanipulator instrument is used6; whereas, other method is a micromanipulator-free SCNT called Handmade cloning (HMC)78. The HMC is preferred due to the low cost of embryo production and less requirement of highly skilled workforce to perform embryo manipulations. The HMC procedure includes five steps which are: (i) removal of genetic material (enucleation) from zona-free oocytes using a small blade, (ii) electro-fusion of donor cells with nucleus-free oocytes, (iii) activation of fused embryos, (iv) in vitro culture of activated embryo for 7 or 8 days, and (v) in vivo transfer of generated blastocysts into foster mothers to deliver cloned calves. Basic differences between classical SCNT and HMC are shown in Table I. The births of healthy calves have been reported in cattle, pig and goat and buffalo using HMC technique3.
| Condition | Classical SCNT | Handmade cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Use of micromanipulator | Yes | No |
| Zona-free | No | Yes |
| Manual enucleation | No | Yes |
| Activation and culture methods | Similar | Similar |
| Problems associated with zona hatching | Yes | No |
| Problems associated with mitochondrial heteroplasmy | No | Yes |
| Comparative cell number in produced blastocysts | Less | High |
| Problems associated with genomic reprogramming | Yes | Yes |
| Skilled workforce manpower to perform experiment | Yes | No |
| Involved cost | High | Less |
Source: Ref. 8
Status of buffalo cloning in India
In India, a simplified HMC, which was earlier demonstrated by Vajta et al9 in cattle has been adopted. The basic method was modified to support the developmental competence of buffalo oocytes and embryos, which resulted in the efficient enucleation, fusion and activation and high blastocyst production rates710. The first live birth of cloned buffalo was reported in 2009 using optimized buffalo HMC method11. Following the birth of first cloned buffalo, several cloned buffaloes were produced in India, and attempts are continued to produce more clones3. Optimized HMC technique has yielded much higher blastocyst production rate than that of IVF technique (35-45% blastocyst rates in case of HMC; whereas, 10-15% in case of IVF embryos); however, the large number of produced blastocysts could not be translated into live clones3. Previous studies in buffalo suggested that cloned embryos exhibited hypermethylated, abnormal histone acetylation and methylation and altered genes expression pattern as compared to IVF embryos12131415. These reports suggest that basic research is needed to understand the epigenetic machinery of somatic cells and cloned embryos to improve the success rate of SCNT.
Ways to correct epigenetic reprogramming
Different approaches have been used to correct the epigenetic reprogramming in cloned embryos such as treatment of somatic cells, oocytes and fused embryos with epigenetic modifiers or with oocytes or stem cells extract, overexpression or suppression of important regulatory genes in somatic cells or one cell stage cloned embryos (Figure). Buffalo somatic cells and/or fused embryos were treated with different epigenetic modulating agents, such as trichostatin A (TSA), 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine (5-aza-dC), valproic acid (VPA) and m-carboxycinnamic acid bishydroxamide (CBHA)14161718. These studies showed that treatment of buffalo donor cells and/or one cell stage fused embryos or both with epigenetic modulators, alone or in combination, resulted in higher blastocyst production rates and lower level of apoptosis in generated cloned blastocysts1415. Future studies are needed to transfer improved blastocysts produced following the treatment of epigenetic modifiers into recipients to improve live birth rates.
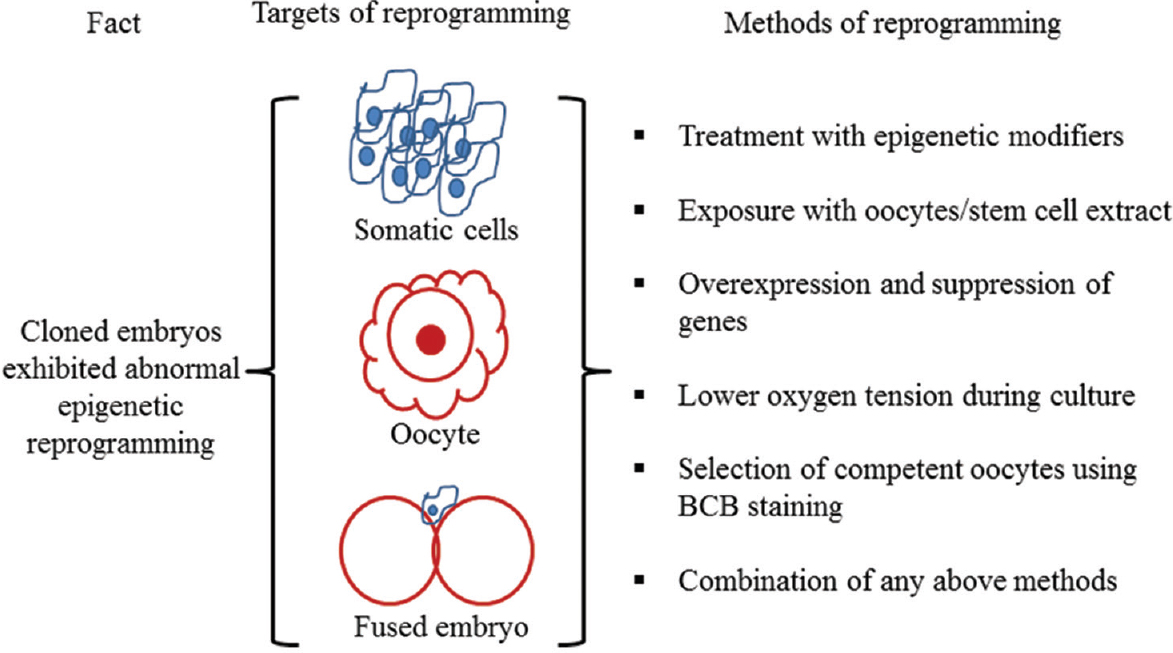
- Different approaches used to correct an epigenetic reprogramming in buffalo cloned embryos. Somatic cell, oocyte, and fused embryo can be treated with any mentioned method either individually or in combination to improve reprogramming. BCB, Brilliant Cresyl Blue.
-
Source: Ref. 3.
Use of epigenetic modifiers in buffalo cloning
Though different epigenetic modifiers were used to correct reprogramming in buffalo embryos; but best results were obtained with the combination of TSA and 5-aza-dC treatments (Table II). Panda et al19 reported that treatment of fused embryos with 500 and 1000 nmol/l of scriptaid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, significantly increased the blastocyst production rate. Furthermore, blastocysts derived from treated groups had higher cell number (339.9±1.4 and 343.4±2.4, respectively) than that of untreated group (150.7±2.0)19. Saini et al14 examined the effects of treatment of donor cells with TSA and 5-aza-dC and found that donor cell treatments altered the expression of epigenetic-related genes, namely HDAC1, DNMT1 and DNMT3a. Treatment with these two epigenetic modifiers also increased the acetylation level of lysine at position 9 or 14 in histone 3 (H3K9/14ac), lysine at position 5 in histone 4 (H4K5ac), lysine at position 18 in histone 3 (H3K18ac) and decreased tri-methylation of lysine at position 27 in histone 3 (H3K27me3) in the cells. Simultaneous treatment of donor cells with TSA (50 nM) and 5-aza-dC (7.5 nM) resulted in improved blastocyst rates, lower apoptotic index and higher level of H3K27me3 in cloned blastocysts14. Subsequently, the same group15 optimized doses of TSA and 5-aza-dC to improve reprogramming in buffalo cloned embryos by examining whether combined treatments of epigenetic modifiers would offer any advantage over treatment with the individual epigenetic modifier. Irrespective of whether donor cells or fused embryos or both treated with 50 nM TSA+7.5 nM 5-aza-dC, the blastocyst rates significantly improved (Table I); low apoptotic index, which was similar to blastocysts produced through in vitro fertilization; and higher level of H3K18ac and lower H3K27me3 level in blastocysts than that of untreated group. This study demonstrated that similar beneficial effects could be obtained by treatment of donor cells or fused embryos or both with 50 nM TSA+7.5 nM 5-aza-dC15. Selokar et al16 used an epigenetic modifier, VPA, another class of histone deacetylase inhibitor, to treat the donor cells for correcting epigenetic reprogramming. This study demonstrated that treatment of donor cells with VPA did not improve the blastocyst production rate. Agrawal et al17 reported that 10 μM of CBHA could be used to improve the blastocyst rates and quality of cloned embryos.
| Epigenetic modifier | Treatment type | Blastocyst rate (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scriptaid (nmol/l) | |||
| 0 | Fused embryos (6 h) | 38 | 19 |
| 500 | 42# | ||
| 1000 | 54# | ||
| TSA (50 nM) + 5-aza-dC (7.5 nM)* | Control | 43 | 15 |
| Cells (24 h prior SCNT) | 71# | ||
| Fused embryos (10 h) | 68# | ||
| Cells + fused embryos | 71# | ||
| Valproic acid (mM) | |||
| 0 | Cells (24 h prior SCNT) | 45 | 16 |
| 1.5 | 49 | ||
| 3.0 | 48 | ||
| 4.5 | 52 | ||
| CBHA (μM) | |||
| 0 | Fused embryos (10 h) | 48.63 | 17 |
| 5 | 52.00 | ||
| 10 | 63.77# | ||
| 20 | 48.32 | ||
| 50 | 54.98 | ||
*Mentioned doses of TSA (trichostatin A) and 5-aza-dC (5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine) were optimized by treating somatic cells, fused embryos or both using different concentrations of these drugs. #Represents the significant improvement in blastocyst production rates than that of the untreated control group. SCNT, somatic cell nuclear transfer; CBHA, m-carboxycinnamic acid bishydroxamide
Beneficial effects are mediated by decreasing DNA and histone methylation and increasing histone acetylation. Treatment of buffalo donor cells or fused embryos or both with epigenetic modulators can be one of the ways to improve the success rate of buffalo SCNT. In addition to the use of epigenetic modifiers, other approaches have also been used such as lower oxygen tension during embryo culture20, use of BCB stating to screen best competent oocytes for the production of cloned embryos21. These approaches also resulted in an improvement in the blastocyst production rates and quality of produced blastocysts; however, more attempts are required to translate in vitro improvements into in vivo developments.
Conclusion
Buffalo cloning is a powerful reproductive tool to multiply elite animals, particularly proven bulls; however, live offspring production efficiency is low which is mainly due to abnormal epigenetic reprogramming. Previous studies demonstrated that abnormal epigenetic reprogramming can be corrected using the treatment of somatic cells or fused embryos with epigenetic modifiers, namely TSA and 5-aza-dC. In Buffalo, limited attempts were made to transfer epigenetically improved blastocysts into recipient animals to examine their in vivo developments; therefore, further studies are required to determine whether the beneficial effects observed in vitro following treatment of epigenetic modifiers would translate to live births.
Financial support & sponsorship:
This work was financially supported by the National Agriculture Innovative Project grants (C 2-1-(5)/2007, C-2067 and 075) to the ABTC, NDRI, Karnal, Haryana.
Conflicts of Interest:
None.
Acknowledgment
Authors thank the past members of buffalo cloning team of the Animal Biotechnology Centre (ABTC), National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), Karnal, Haryana.
References
- Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature. 1997;385:810-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- An update: Reproductive handmade cloning of water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Anim Reprod Sci. 2018;197:1-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cloning of buffalo, a highly valued livestock species of South and Southeast Asia: Any achievements? Cell Reprogram. 2018;20:89-98.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rabbit somatic cell cloning: Effects of donor cell type, histone acetylation status and chimeric embryo complementation. Reproduction. 2007;133:219-30.
- [Google Scholar]
- Buffalos (Bubalus bubalis) cloned by nuclear transfer of somatic cells. Biol Reprod. 2007;77:285-91.
- [Google Scholar]
- Hand-made cloned buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos: Comparison of different media and culture systems. Cloning Stem Cells. 2008;10:435-42.
- [Google Scholar]
- Handmade cloning: The future way of nuclear transfer? Trends Biotechnol. 2007;25:250-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Effect of post-fusion holding time, orientation and position of somatic cell-cytoplasts during electrofusion on the development of handmade cloned embryos in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Theriogenology. 2012;78:930-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Establishment of trophectoderm cell lines from buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos of different sources and examination of in vitro developmental competence, quality, epigenetic status and gene expression in cloned embryos derived from them. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0129235.
- [Google Scholar]
- Use of peripheral blood for production of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos by handmade cloning. Theriogenology. 2016;86:1318-240.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) donor cells with trichostatin A and 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine alters their growth characteristics, gene expression and epigenetic status and improves the in vitro developmental competence, quality and epigenetic status of cloned embryos. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016;28:824-37.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of donor cells and reconstructed embryos with a combination of trichostatin-A and 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine improves the developmental competence and quality of buffalo embryos produced by handmade cloning and alters their epigenetic status and gene expression. Cell Reprogram. 2017;19:208-15.
- [Google Scholar]
- Valproic acid increases histone acetylation and alters gene expression in the donor cells but does not improve the in vitro developmental competence of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos produced by hand-made cloning. Cell Reprogram. 2017;19:10-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- M-carboxycinnamic acid bishydroxamide improves developmental competence, reduces apoptosis and alters epigenetic status and gene expression pattern in cloned buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos. Reprod Domest Anim. 2018;53:986-96.
- [Google Scholar]
- Epigenetic alteration of donor cells with histone deacetylase inhibitor m-carboxycinnamic acid bishydroxymide improves the in vitro developmental competence of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) cloned embryos. Cell Reprogram. 2018;20:76-88.
- [Google Scholar]
- Effect of scriptaid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, on the developmental competence of handmade cloned buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos. Theriogenology. 2012;77:195-200.
- [Google Scholar]
- Low oxygen tension improves developmental competence and reduces apoptosis in hand-made cloned buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos. Livest Sci. 2015;172:106-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Buffalo embryos produced by handmade cloning from oocytes selected using brilliant cresyl blue staining have better developmental competence and quality and are closer to embryos produced by in vitro fertilization in terms of their epigenetic status and gene expression pattern. Cell Reprogram. 2015;17:141-50.
- [Google Scholar]






